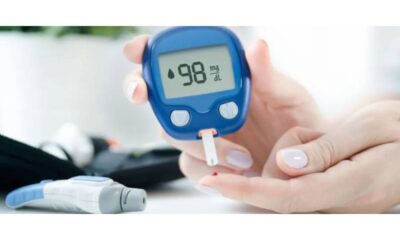
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions of people worldwide. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of type 2 diabetes, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies to empower you with knowledge and control.
Understanding Blood Sugar and Insulin: The Core Players
Before delving into type 2 diabetes, it’s crucial to understand the role of blood sugar (glucose) and insulin in our bodies:
- Blood Sugar (Glucose): The primary source of energy for our cells. Foods you eat are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream.
- Insulin: A hormone produced by the pancreas that acts like a key, unlocking the doors of your cells and allowing glucose to enter for energy production.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
In type 2 diabetes, the body either develops insulin resistance or doesn’t produce enough insulin. This leads to a buildup of glucose in the bloodstream instead of entering the cells, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Excess weight, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, and smoking are significant risk factors.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnicities are at a higher risk.
- Prediabetes: A condition with higher-than-normal blood sugar levels but not yet considered type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes if left unmanaged.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Early symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be subtle and easily overlooked. Here are some key signs to watch out for:
- Increased thirst and urination: The body tries to expel excess sugar through urine, leading to frequent urination and increased thirst.
- Excessive hunger: Cells are starved for energy due to the inability to utilize blood sugar effectively, leading to increased hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss: The body might break down muscle tissue for energy when glucose utilization is impaired.
- Fatigue and tiredness: Cells deprived of glucose experience a lack of energy, leading to fatigue.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the lenses in the eyes, causing blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair circulation and healing processes.
- Frequent infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult your doctor for a diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
Left untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Nerve damage (neuropathy): High blood sugar can damage nerves, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, and digestive problems.
- Kidney disease: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye problems: Diabetes can increase the risk of glaucoma, cataracts, and even blindness.
- Foot problems: Nerve damage and poor circulation in the feet can increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections, potentially leading to amputation.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Management
Early diagnosis and effective management of type 2 diabetes are crucial to prevent complications and improve overall health.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Several tests can diagnose type 2 diabetes:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): Measures blood sugar levels after a night of fasting.
- Hemoglobin A1c (A1c): Indicates average blood sugar control over a 2-3 month period.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Measures blood sugar levels after drinking a sugary drink.
Treatment and Management Strategies
There’s no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be effectively managed through a multi-pronged approach:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit sugary drinks, processed foods, and saturated fats.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing even a moderate amount of weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Medications: Several medications can help manage type 2 diabetes, including oral medications and injectable insulin. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate medication regimen based on your individual needs and severity of the condition. Here are some common types:
- Metformin: The first-line medication for many individuals with type 2 diabetes. It helps the body use insulin more effectively and reduces glucose production by the liver.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: These medications work by slowing the breakdown of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: These medications help the kidneys remove excess sugar from the bloodstream through urine.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These injectable medications mimic a natural gut hormone that stimulates insulin release and reduces glucagon secretion, leading to lower blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Therapy: In some cases, injectable insulin might be necessary to maintain good blood sugar control.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Self-monitoring of blood sugar levels using finger pricks and a glucometer or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) is crucial for informed decision-making about diet, exercise, and medication adjustments.
- Education and Support: Learning about diabetes management, self-care strategies, and joining support groups can empower individuals with knowledge and emotional support.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Type 2 Diabetes
A diagnosis of type 2 diabetes doesn’t have to limit your life. By implementing these management strategies and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can effectively control your blood sugar and live a full and vibrant life. Here are some additional tips:
- Develop a positive mindset: Focus on progress, not perfection, and celebrate your achievements along the way.
- Prioritize stress management: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and blood sugar control.
- Don’t neglect dental hygiene: Diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease. Maintain good oral hygiene practices.
- Schedule regular checkups: Regular visits with your doctor are essential for monitoring your condition and adjusting your treatment plan as needed.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. With knowledge, dedication, and the support of your healthcare team, you can thrive with type 2 diabetes.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor to create a personalized diabetes management plan.
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago