Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions globally, disrupts the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar (glucose). However, this umbrella term encompasses two distinct variations: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective diagnosis, management, and ultimately, living well with the condition.
This article delves into the complexities of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, dissecting the underlying causes, exploring the spectrum of symptoms, and unveiling the unique management strategies for each. We’ll also explore the emotional and psychological aspects of living with these conditions, shedding light on the human experience beyond the medical jargon.
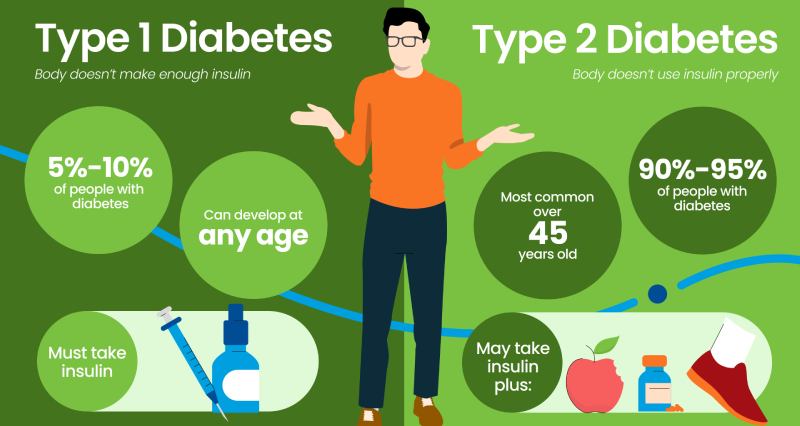
The Root of the Problem – Understanding the Cause of Each Type
- Type 1 Diabetes: An Autoimmune Assault
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. In this case, the target is the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This attack disrupts insulin production, leaving the body unable to effectively usher glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy. The exact trigger for this autoimmune response remains unclear, but genetics and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A Resistance and Deficiency Tango
Type 2 diabetes stems from a two-pronged problem: insulin resistance and insulin deficiency. The body’s cells become resistant to insulin’s message, hindering glucose uptake. Additionally, the pancreas, while still producing insulin, may not be able to keep pace with the body’s growing demand, leading to a relative deficiency. Unlike Type 1, genetics and lifestyle choices, particularly excess weight and physical inactivity, are significant risk factors for Type 2 diabetes.
A Tale of Two Symptoms – Unveiling the Warning Signs
The early signs of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can overlap, but there are some key distinctions to be aware of:
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme hunger (polyphagia)
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
These symptoms often develop rapidly, within weeks or even days, as insulin production plummets.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
Symptoms for Type 2 diabetes can be subtle and may go unnoticed for years, particularly in the early stages.
Charting a Course – Management Strategies for Each Type
Living with diabetes requires ongoing management to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. The approaches differ between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes:
For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, insulin is a lifeline. Management revolves around:
For children diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, the constant vigilance required for management can disrupt daily life and cause anxiety. Families may struggle to adjust to the demands of the condition.
People with Type 2 diabetes may experience feelings of guilt or shame, particularly if the diagnosis is attributed to lifestyle choices. Fear of complications and the constant pressure of managing the condition can also take a toll on mental well-being.
Finding Support and Embracing Resilience
Fortunately, there’s a wealth of resources available for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics to navigate the emotional and psychological challenges.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand the complexities of living with diabetes can be invaluable. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, find encouragement, and learn coping strategies.
- Mental Health Professionals: Therapists can provide individual or family counseling to address anxieties, fears, and adjustment difficulties related to diabetes management.
- Diabetes Educators: Certified diabetes educators can offer personalized guidance on managing the condition effectively and developing healthy coping mechanisms.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Diabetes
While diabetes presents challenges, it doesn’t have to define your life. By understanding the specific type of diabetes you have, implementing effective management strategies, and prioritizing your emotional well-being, you can live a full and rewarding life.
Here are some additional points to consider adding:
- Technological Advancements: Explore advancements in diabetes technology, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and automated insulin delivery systems, that can improve blood sugar control and simplify management.
- The Future of Diabetes Research: Briefly touch on ongoing research in areas like islet cell transplantation for Type 1 diabetes and potential cures or preventative measures for both types.
- Success Stories: Share stories of individuals who have thrived with diabetes. This can provide inspiration and hope for those newly diagnosed or struggling with management.
Conclusion
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes may be distinct conditions, but they share the common thread of requiring ongoing management. However, with a proactive approach, a supportive network, and a commitment to healthy living, you can successfully manage your diabetes and live a fulfilling life.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology20 hours ago
Diabetology20 hours ago
 Diabetology3 hours ago
Diabetology3 hours ago
 Diabetology3 hours ago
Diabetology3 hours ago