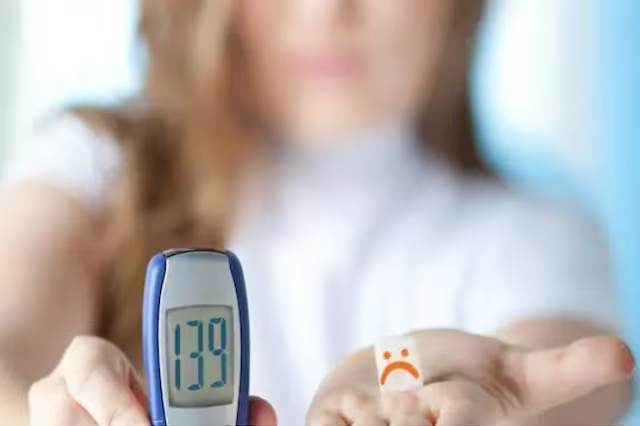
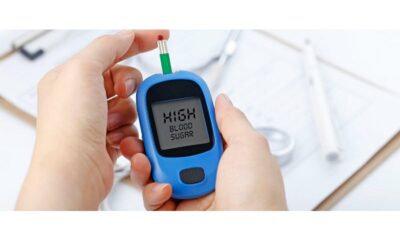
Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, is the main source of energy for your body. It comes from the carbohydrates you consume, which are broken down into glucose and transported through your bloodstream to your cells. Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for those with diabetes or prediabetes. This guide delves into understanding blood sugar levels, their significance, and how to interpret them for optimal health.
The Role of Blood Sugar
Blood sugar plays a vital role in various bodily functions:
- Energy Production: Glucose is the primary fuel for your cells, powering muscles, organs, and the brain.
- Cellular Function: It’s essential for proper cell function and communication throughout the body.
- Brain Function: Glucose is crucial for maintaining cognitive function, focus, and memory.
- Hormonal Regulation: Blood sugar levels influence the release of hormones like insulin and glucagon, which regulate metabolism.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Balance
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar balance is crucial for preventing various health problems. Here’s why:
- Chronic Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): Over time, consistently high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, blood vessels, and organs, leading to complications like neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and heart disease.
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): When blood sugar levels drop too low, it can cause symptoms like sweating, shakiness, dizziness, and confusion. In severe cases, it can lead to seizures or coma.
- Diabetes: Chronic hyperglycemia is a hallmark of diabetes, a group of conditions characterized by impaired insulin production or resistance. This can lead to a cascade of health problems.
Understanding Blood Sugar Measurements
Blood sugar levels are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Knowing these units and interpreting your results is crucial:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: This test measures your blood sugar level after not eating for at least 8 hours, typically done first thing in the morning.
- Random Blood Sugar: This test can be done at any time, regardless of when you last ate. It provides a snapshot of your blood sugar at that moment.
- A1C Test: This test measures the percentage of red blood cells coated with sugar, reflecting your average blood sugar control over the past 2-3 months.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Levels
Here’s a breakdown of blood sugar level ranges and their interpretations, with the caveat that these are general guidelines, and consulting your doctor for personalized advice is essential:
Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) Interpretation
Below 70 | Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) 70-99 | Normal fasting blood sugar 100-125 | Prediabetes 126 or higher on two separate tests | Diabetes 140 or below (1-2 hours after eating) | Normal blood sugar after eating Below 100 (pregnant women) | Normal fasting blood sugar for pregnant women
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence your blood sugar levels:
- Diet: The type and amount of carbohydrates you consume significantly impact blood sugar. Sugary foods and refined carbohydrates cause rapid spikes, while complex carbohydrates like whole grains provide sustained energy.
- Exercise: Physical activity helps your body utilize glucose more efficiently, leading to lower blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, like steroids and some antidepressants, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels by triggering the release of stress hormones like cortisol.
- Hormonal Changes: Menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and certain hormonal conditions can impact blood sugar control.
- Illness: Infections and illnesses can raise blood sugar levels due to the body’s stress response.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Here are some key strategies to manage blood sugar levels effectively:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management: If overweight or obese, losing weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Medication Management: If prescribed diabetes medications like insulin or oral medications, adhere to your doctor’s instructions.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress hormones and improve blood sugar control.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels according to your doctor’s recommendations. This allows for adjustments to your diet, exercise, or medications as needed.
Living with Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Living with healthy blood sugar levels goes beyond just monitoring and management. It’s about incorporating these practices into your lifestyle for long-term well-being. Here are some additional tips:
- Planning and Preparation: Plan your meals and snacks in advance to ensure healthy choices are readily available.
- Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself. There will be days when blood sugar levels fluctuate. The key is to learn from experiences and make adjustments.
- Support System: Connect with a diabetes support group or find a healthcare professional specializing in diabetes management.
- Regular Checkups: Schedule regular appointments with your doctor to monitor your progress, address any concerns, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
By understanding your blood sugar levels, making healthy lifestyle changes, and working with your healthcare team, you can effectively manage your blood sugar and live a fulfilling life.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago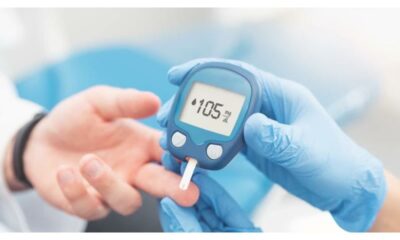
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago