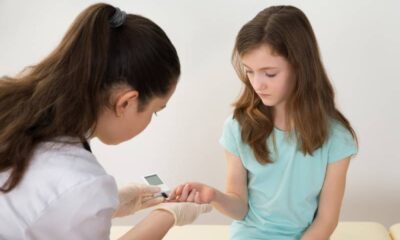
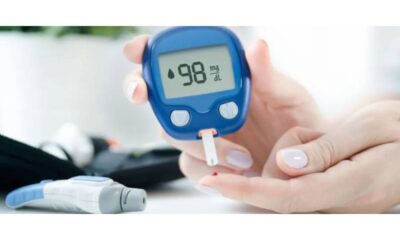
Receiving a diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) for your child can be overwhelming. This lifelong condition requires constant vigilance and management, impacting your entire family. However, with knowledge, effective strategies, and a strong support system, you can empower your child to thrive. This guide explores parenting strategies for managing T1D and the various support systems available to you on this journey.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
Unlike Type 2 Diabetes, T1D is an autoimmune disease where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels. Without sufficient insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to various health complications if left untreated.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Early detection is vital. Be aware of these signs and symptoms in your child:
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Unintended weight loss
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Frequent infections
If you suspect T1D, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Treatment and Management
While there’s no cure for T1D, effective management keeps blood sugar levels within a healthy range. The primary treatments involve:
- Insulin injections: Several types of insulin are available, requiring careful administration based on your child’s needs.
- Blood sugar monitoring : Regularly checking blood sugar with a glucose meter helps determine insulin dosage adjustments.
- Carbohydrate counting: Understanding how carbohydrates affect blood sugar allows for appropriate insulin dosing before meals.
- Healthy eating: A balanced diet with an emphasis on whole foods promotes optimal blood sugar control.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise helps manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity.
Parenting Strategies
- Education is key: Empower yourself and your child with knowledge about T1D. Attend diabetes education classes, and involve your child in learning about their condition.
- Develop a routine: Establish a consistent schedule for meals, blood sugar checks, and insulin administration.
- Positive reinforcement: Focus on celebrating successes and offering encouragement. Avoid negativity or blame when managing blood sugar levels.
- Communication and teamwork: Open communication with your child is crucial. Work together as a team to manage T1D effectively.
- Building independence: As your child matures, gradually encourage them to become more responsible for their diabetes management.
- Maintaining normalcy: While T1D requires adjustments, strive to maintain normalcy in your child’s life. Incorporate diabetes management into daily activities without letting it dominate life experiences.
Support Systems
You are not alone in this journey. Several support systems can provide invaluable resources and guidance:
- Healthcare team: Your child’s doctor, endocrinologist, diabetes educator, and dietician form a crucial support team. They offer expert advice, address concerns, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Support groups: Connecting with other families managing T1D can be incredibly helpful. Share experiences, learn from each other, and gain emotional support.
- Online communities: Numerous online forums and social media groups connect families with T1D. Access information, share experiences, and build a virtual support network.
- Camps and programs: Specialized camps and programs offer a unique environment for children with T1D. They learn diabetes management skills, connect with peers, and build confidence in a supportive setting.
- Mental health support: Living with a chronic condition can be emotionally challenging. Consider seeking mental health support for yourself or your child if needed.
Additional Considerations
- School communication: Work with your child’s school to develop a diabetes management plan. Educate teachers about T1D and ensure your child has access to blood sugar monitoring and medication when needed.
- Travel and social events: Plan ahead for travel and social events. Pack necessary supplies, adjust insulin doses if necessary, and communicate your child’s needs to those involved.
- Financial assistance: Managing T1D can be expensive. Explore financial assistance programs to help with the cost of insulin, supplies, and medical care.
Conclusion
Raising a child with T1D can be challenging, but with dedication, a positive approach, and the right support systems, you can help your child live a healthy and fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone. Embrace the available resources, empower your child, and navigate this journey together as a team.
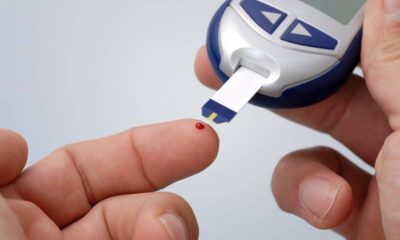
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 General Medicine9 hours ago
General Medicine9 hours ago