Diabetology
The Ultimate Guide to Diabetes Self-Care: Take Charge of Your Health
Published
2 years agoon
By
Robert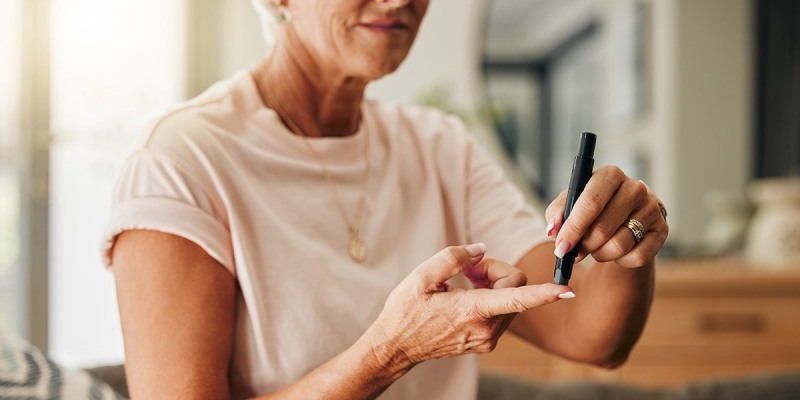
Diabetes may be a chronic condition, but it doesn’t have to define your life. By embracing self-care, you take control of your health and empower yourself to live a vibrant, fulfilling life. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to become an expert in managing your diabetes.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Self-Care
- What is Self-Care?
- Define self-care as the proactive management of your diabetes through daily decisions and actions.
- Explain how self-care empowers you to become a partner in your healthcare journey.
- The Pillars of Self-Care:
- Introduce the four key pillars of effective self-care: diet, exercise, medication management, and blood sugar monitoring.
- Emphasize the interconnectedness of these pillars and how they work together for optimal health.
Taking Charge of Your Diet:
- Food as Medicine: Explain the crucial role of a healthy diet in maintaining blood sugar control.
- Building a Balanced Plate:
- Discuss the importance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fat) and fiber in a diabetic diet.
- Provide guidance on portion control, carbohydrate counting (optional), and reading food labels effectively.
- Deconstructing Sugar Content:
- Explain the different types of sugars (natural vs. added) and their impact on blood sugar.
- Offer tips on identifying hidden sugars in processed foods and making healthy substitutions.
- Meal Planning and Snacking Strategies:
- Guide readers on creating personalized meal plans considering preferences and dietary needs.
- Provide tips for healthy snacking throughout the day to maintain blood sugar stability.
- Offer sample meal plans for different dietary patterns (vegetarian, low-carb, etc.)
Moving Your Body for Better Health:
- The Power of Exercise: Explain the numerous benefits of physical activity for blood sugar control, weight management, and overall well-being.
- Finding Your Fitness Fit:
- Discuss different types of exercises suitable for various fitness levels (aerobic, strength training, flexibility).
- Offer tips on incorporating physical activity into a busy schedule, even with limited time.
- Provide sample workout routines that can be modified based on individual needs.
- Staying Motivated:
- Address common challenges with exercise and offer strategies for staying motivated.
- Encourage finding activities you enjoy, incorporating social elements (group fitness classes), and celebrating achievements.
- Overcoming Activity Limitations:
- Discuss how to adapt exercise routines for individuals with physical limitations or injuries.
- Highlight the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for safe and effective exercise programs.
Mastering Medication Management:
- Understanding Your Medications:
- Explain different types of diabetes medications (oral medications, injectable insulin) and their mechanisms of action.
- Discuss potential side effects and the importance of medication adherence.
- Building a Medication Routine:
- Offer tips on creating a medication schedule that integrates seamlessly with your daily life.
- Encourage using pill organizers, setting reminders, and discussing any concerns with your doctor.
- Traveling with Medications:
- Provide guidance on safely storing and transporting medications when traveling.
- Discuss obtaining necessary refills and documentation for international travel.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar Levels:
- Knowing Your Numbers: Explain the importance of self-monitoring blood sugar (SMBG) and using a glucometer effectively.
- Frequency and Timing:
- Discuss how often to monitor blood sugar based on diabetes type, medications, activity level, and individual needs.
- Explain the significance of checking blood sugar before meals, after meals, and at bedtime (when applicable).
- Interpreting Your Results:
- Explain what blood sugar readings mean and how they relate to your overall health and treatment plan.
- Discuss target blood sugar ranges and the importance of keeping them in check.
Beyond the Numbers: Emotional Well-being
- The Emotional Impact: Acknowledge the emotional challenges that can accompany diabetes (stress, anxiety, depression).
- Coping Mechanisms: Offer a variety of coping mechanisms to manage diabetes-related stress and emotions.
- This could include relaxation techniques (deep breathing, meditation), mindfulness practices, journaling, and seeking emotional support.
Building a Support System:
- The Power of Community: Explain the benefits of having a strong support system for managing diabetes.
- Finding Your Support Network:
- Discuss different sources of support, including family, friends, healthcare providers, diabetes support groups, and online communities.
- Encourage readers to connect with others who understand the challenges and triumphs of living with diabetes.
Maintaining Motivation and Overcoming Challenges:
- Setting SMART Goals:
- Introduce the concept of SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) for diabetes self-care.
- Guide readers on setting realistic and achievable goals that celebrate progress.
- Staying Motivated in the Long Run:
- Address the natural dips in motivation that can occur over time.
- Offer tips on finding inspiration, like reading success stories of others with diabetes or setting small rewards.
- Encourage focusing on the positive outcomes of self-care and the long-term benefits for your health.
The Future of Diabetes Management:
- The Importance of Proactive Healthcare: Emphasize the importance of attending regular doctor appointments and preventative screenings.
- Early Detection and Management:
- Discuss the benefits of early detection and treatment of potential diabetes complications (eye disease, nerve damage, foot problems).
- Explain the role of regular screenings in maintaining long-term health.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Diabetes:
- Addressing Common Challenges:
- Offer solutions for managing diabetes on special occasions (holidays, travel).
- Discuss healthy coping mechanisms for stressful situations.
- Staying Active and Engaged:
- Highlight success stories of people living well with diabetes.
- Encourage readers to pursue their passions and hobbies, demonstrating that diabetes doesn’t limit possibilities.
- Building Confidence and Self-Esteem:
- Address the potential for negative self-image related to diabetes.
- Offer tips for body positivity and self-acceptance despite the challenges.
- Encourage readers to celebrate their achievements and focus on their strengths.
The Future of Diabetes Management:
- Emerging Technologies:
- Briefly discuss advancements in diabetes technology, like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and automated insulin delivery pumps.
- Offer a hopeful outlook on potential future breakthroughs in treatment and prevention.
Conclusion: Your Empowered Health Journey
- By adopting these self-care strategies, you are taking control of your diabetes and creating a path toward a healthier, happier you. Remember, you are not alone on this journey. With a supportive network, a positive attitude, and the knowledge you’ve gained from this guide, you can achieve optimal health and live a fulfilling life.
Disclaimer:
- Note that this information is intended for general knowledge and should not replace professional medical advice.
- Encourage readers to consult with their healthcare providers for personalized guidance on managing their diabetes.
Continue Reading
You may like
-
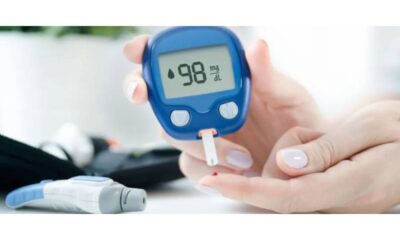

Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
-


Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Range and How to Maintain It
-


How to Monitor Blood Sugar at Home: A Beginner’s Guide
-


How Blood Sugar Monitoring Can Help with Prediabetes
-


Does Coffee Impacting Your Blood Sugar Levels?
-


Diabetes Self-Care: Essential Tips for Better Blood Sugar Control and Well-Being
The Latest News
- Best Low-Glycemic Sweeteners for Diabetics: A Healthier Choice
- Effect of Physical Activity on Blood Sugar and Diabetes
- High Blood Sugar Symptoms: 10 Common Signs You May Have Diabetes
- Daily Routine for Diabetics: A Complete Guide to a Healthy, Balanced Day
- Morning Routine for Diabetics: Simple Steps to Stabilize Blood Sugar
- Diabetes and Heart Disease Connection: Early Signs, Risks & Prevention
- Reversing Type 2 Diabetes: What the Latest Research Says in 2025

Diabetology6 days ago
Best Low-Glycemic Sweeteners for Diabetics: A Healthier Choice

Diabetology2 weeks ago
Effect of Physical Activity on Blood Sugar and Diabetes
Diabetology2 weeks ago
High Blood Sugar Symptoms: 10 Common Signs You May Have Diabetes

Pulmonology2 years ago
Lung growth invading Treg have different transcriptional profiles and capability connected to designated spot bar reaction

Dermatology2 years ago
Psoriasis be treatment by adjuvant Salicylic acid, ceramides as this containing lotions

Dermatology2 years ago

