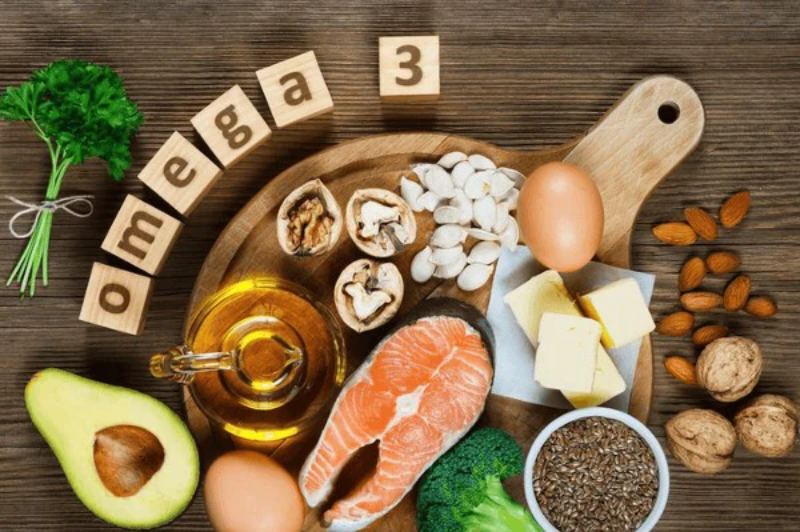
1. Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity
One of the key challenges for people with type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance, where the body’s cells fail to respond properly to insulin. Research suggests that omega-3s may help improve insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to absorb glucose more efficiently and reducing blood sugar spikes.
2. Reducing Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is closely linked to insulin resistance and the progression of diabetes. Omega-3 fatty acids possess strong anti-inflammatory properties, which may help lower levels of inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP). By reducing inflammation, omega-3s can support better metabolic function and reduce complications associated with diabetes.
3. Supporting Heart Health
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Omega-3s contribute to heart health by:
- Lowering triglyceride levels, which are often elevated in diabetics
- Increasing good cholesterol (HDL) and reducing bad cholesterol (LDL)
- Reducing blood pressure and preventing arterial blockages
4. Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy, a condition where high blood sugar damages nerves, affects many individuals with diabetes. Symptoms include pain, tingling, and numbness in the hands and feet. Omega-3s may help protect nerve function and promote nerve regeneration, potentially reducing neuropathic symptoms over time.
5. Supporting Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical for diabetes management. Omega-3s may aid in appetite control and fat metabolism, helping individuals achieve a healthier body weight, which in turn can improve blood sugar control.
Best Sources of Omega-3 for Diabetes
1. Fatty Fish (Best Animal Sources)
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Tuna
- Trout
2. Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
For those who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, the following foods provide ALA (Alpha-linolenic acid), a type of omega-3 that the body can partially convert into the more active forms, EPA and DHA:
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
- Walnuts
- Hemp seeds
3. Omega-3 Supplements
Fish oil, krill oil, and algae-based omega-3 supplements are widely available. It’s important to choose high-quality, purified supplements that have been tested for contaminants like mercury. Always consult a doctor before starting supplementation, especially if taking blood-thinning medications.
How to Incorporate Omega-3s Into Your Diet
- Eat fatty fish at least twice a week
- Add flaxseeds or chia seeds to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal
- Use walnuts as a healthy snack or in salads
- Replace cooking oils with flaxseed oil or canola oil
- Consider supplements if dietary intake is insufficient
Precautions and Considerations
While omega-3s offer many benefits, excessive consumption may lead to blood thinning, which could be a concern for individuals on anticoagulant medications. Additionally, certain fish species may contain mercury, so it’s best to opt for low-mercury fish like salmon and sardines.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids play a valuable role in diabetes management by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, and protecting heart and nerve health. Including natural sources of omega-3 in your diet or taking high-quality supplements can be a beneficial addition to a comprehensive diabetes care plan. However, always consult a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago