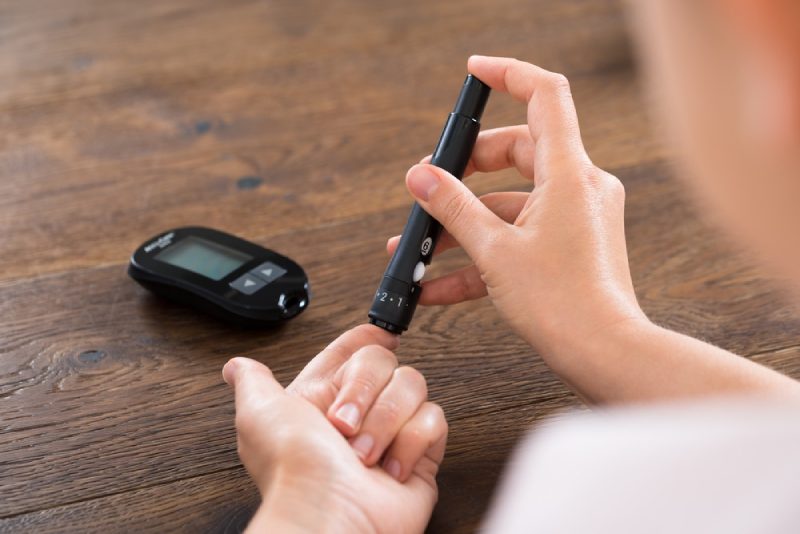
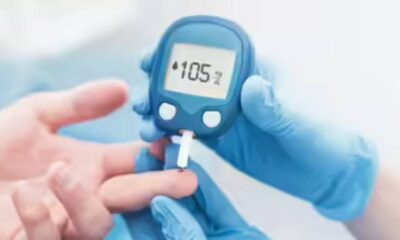
For millions of people worldwide, diabetes is a constant companion. While type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, type 2 diabetes, often linked to lifestyle factors, is a growing concern. Regardless of the type, effectively managing blood sugar levels is paramount in preventing a cascade of complications that can significantly impact quality of life. This is where blood sugar monitoring emerges as a silent guardian, empowering individuals with diabetes to take an active role in their health. This article delves into the importance of blood sugar monitoring, exploring its benefits in preventing diabetes complications and offering practical guidance for successful implementation.
The Diabetes Landscape: A Balancing Act
Our bodies rely on glucose, a simple sugar, for energy. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, acts as a key, allowing glucose to enter cells and be used for energy. In diabetes, this delicate balance is disrupted.
- Type 1 Diabetes: The body doesn’t produce enough insulin, leading to chronically high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
- Type 2 Diabetes: Cells become resistant to insulin, or the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, again resulting in hyperglycemia.
Chronic hyperglycemia, if left unchecked, can damage various organs and tissues over time, leading to a range of complications, including:
- Diabetic neuropathy: Nerve damage that can cause pain, numbness, and tingling, particularly in the feet and legs.
- Diabetic retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of the eye, which can lead to vision loss.
- Diabetic nephropathy: Kidney damage that can eventually lead to kidney failure.
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: A Window into Your Health
Blood sugar monitoring allows individuals with diabetes to measure their blood sugar levels at home. This provides valuable real-time data on how their body responds to food, exercise, and medications. There are two main methods for blood sugar monitoring:
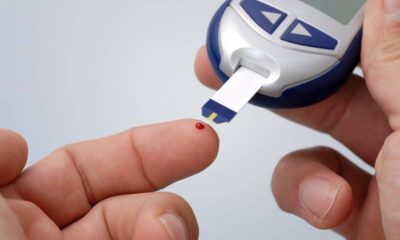
- Finger Prick Testing: A small drop of blood is drawn from a fingertip using a lancing device and tested with a glucometer, a portable device that displays the blood sugar level.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): A sensor inserted under the skin transmits blood sugar data wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone app, providing a more continuous picture of blood sugar trends throughout the day and night.
The Power of Blood Sugar Monitoring: Preventing Complications
Regular blood sugar monitoring offers a multitude of benefits for people with diabetes:
- Improved Glycemic Control: By monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can adjust their diet, exercise routines, and medication dosages to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range. This helps prevent chronic hyperglycemia, the underlying cause of most diabetes complications.
- Early Detection of Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia: Blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day. Monitoring allows for early detection of both high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), enabling prompt intervention to prevent serious health consequences.
- Informed Decision-Making: Blood sugar data empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their daily routines. For example, they can adjust meal portions, choose appropriate exercise intensity, and manage stress levels based on their blood sugar readings.
- Motivation and Empowerment: Seeing the impact of lifestyle choices on blood sugar levels can be a powerful motivator for maintaining healthy habits. This sense of control over their health can be empowering for individuals with diabetes.
- Improved Communication with Healthcare Providers: Regular blood sugar monitoring provides valuable data for healthcare providers to assess diabetes management and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
A Roadmap to Effective Blood Sugar Monitoring:
For blood sugar monitoring to be truly effective, a personalized approach is essential. Here are some key considerations:
- Frequency of Monitoring: The recommended frequency of blood sugar monitoring varies depending on the type of diabetes, severity, and treatment plan. Consult your doctor to determine the optimal monitoring schedule for you.
- Setting Goals: Working with your doctor, set realistic and achievable blood sugar goals. Regularly monitoring your blood sugar allows you to track your progress towards these goals.
- Understanding Your Numbers: Learn how your blood sugar levels typically respond to food, exercise, and medications. This knowledge helps you anticipate fluctuations and make adjustments accordingly.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain a log of your blood sugar readings, including the time, food intake, and any other relevant factors. This information provides valuable insights and helps identify patterns.
- Overcoming Challenges: Blood sugar monitoring can feel like a burden at times. Discuss any challenges you face with your doctor and seek support groups or online resources for motivation.
Blood Sugar Monitoring for Different Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Generally requires more frequent monitoring, often before meals, before bed, and sometimes after meals or during exercise, depending on the individual and their treatment plan.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The frequency can vary depending on factors like medication, overall glycemic control, and individual needs. It might range from a few times a day to more frequent monitoring during periods of illness or medication changes.
Technological Advancements in Blood Sugar Monitoring:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: These offer a more comprehensive picture of blood sugar trends by providing real-time data throughout the day and night. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those struggling with frequent blood sugar fluctuations.
- Smart Meter Integration: Some glucometers connect with smartphones or apps, allowing for easier data tracking, analysis, and sharing with healthcare providers.
Beyond Monitoring: A Holistic Approach
While blood sugar monitoring is a powerful tool, it’s just one piece of the puzzle in managing diabetes effectively. A comprehensive approach that incorporates the following is crucial:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. Limit added sugars, processed foods, and unhealthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity as recommended by your doctor. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
- Weight Management: If overweight or obese, losing even a moderate amount of weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen blood sugar control. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to manage stress effectively.
- Medication Adherence: Taking medications as prescribed by your doctor is crucial for maintaining good blood sugar control.
Conclusion: A Lifelong Journey of Empowerment
Living with diabetes requires ongoing commitment and effort. Blood sugar monitoring empowers you to take an active role in managing your health and preventing complications. By working closely with your healthcare team, implementing a personalized approach to blood sugar monitoring, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can navigate your diabetes journey with confidence and live a fulfilling life.
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago