Introduction
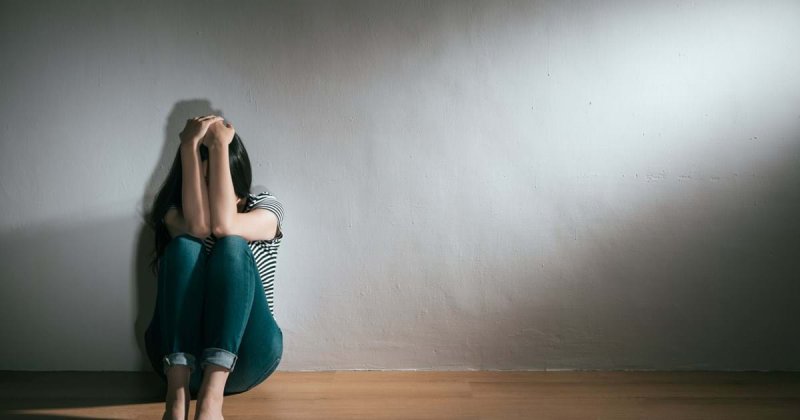
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the physical aspects of diabetes—such as blood sugar management, dietary restrictions, and medication—are often emphasized, the mental health impact of living with this disease can be just as significant. This article explores the connection between diabetes and mental health, the emotional challenges faced by individuals with diabetes, and effective coping strategies along with available support resources.
The Psychological Burden of Diabetes
Living with diabetes can lead to various psychological issues, including anxiety, depression, and stress. According to research, individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing mental health disorders compared to the general population. The daily management of diabetes can be overwhelming, leading to a constant cycle of worry about blood sugar levels, potential complications, and the implications of dietary choices.
- Anxiety and Diabetes
- Individuals may experience anxiety related to managing their condition, fear of complications, or social situations involving food.
- Diabetes-related anxiety can manifest as obsessive thoughts about food and blood sugar, often leading to burnout.
- Depression and Diabetes
- Depression is prevalent among individuals with diabetes. The chronic nature of the disease and the lifestyle changes required can contribute to feelings of hopelessness and fatigue.
- Studies indicate that depression can negatively affect diabetes management, leading to poorer health outcomes.
- Stress and Diabetes
- The day-to-day stress of managing diabetes can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which may negatively impact blood sugar control.
- Stress can trigger emotional eating, which can further complicate diabetes management.
Recognizing the Signs
Understanding the signs of mental health issues related to diabetes is crucial for early intervention. Symptoms may include:
- Persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness
- Increased irritability or mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Withdrawal from social activities and relationships
- Changes in sleeping or eating patterns
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare professional.
Coping Strategies
Implementing effective coping strategies can significantly improve mental well-being for individuals living with diabetes. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Establish a Routine
- Creating a daily schedule that includes time for meals, exercise, medication, and relaxation can help individuals feel more in control.
- Routines can reduce uncertainty and make managing diabetes feel more manageable.
- Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
- Mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety.
- Incorporating relaxation techniques into daily life can enhance emotional resilience.
- Engage in Physical Activity
- Regular exercise not only helps manage blood sugar levels but also boosts mood by releasing endorphins.
- Finding an enjoyable physical activity, such as walking, dancing, or swimming, can make it easier to stick to an exercise routine.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Eating a balanced diet can positively influence mood and energy levels.
- Working with a registered dietitian can help individuals develop meal plans that suit their dietary needs and preferences.
- Set Realistic Goals
- Setting achievable goals for diabetes management can help prevent feelings of failure or frustration.
- Celebrate small victories to boost motivation and self-esteem.
- Stay Connected
- Maintaining social connections is vital for emotional well-being. Reach out to friends, family, or support groups to share experiences and feelings.
- Engaging in community activities can also provide a sense of belonging and support.
- Limit Information Overload
- With the abundance of information available online, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. Limit the amount of research you do and focus on credible sources.
- Consider discussing any concerns or questions with a healthcare provider rather than relying solely on online information.
Seeking Professional Help
If coping strategies are not enough to alleviate mental health concerns, it may be time to seek professional help. Mental health professionals can provide various forms of support, including:
- Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has shown effectiveness in treating anxiety and depression in individuals with diabetes. Therapy can help address negative thought patterns and develop coping skills.
- Support Groups: Joining a diabetes support group can connect individuals with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences can provide comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage anxiety or depression. A healthcare provider can help assess the situation and prescribe appropriate treatments.
Support Resources
There are numerous resources available for individuals living with diabetes to enhance their mental health:
- Diabetes Organizations:
- The American Diabetes Association (ADA) offers a wealth of information on diabetes management, including mental health resources and support.
- Mental Health Resources:
- The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) provides resources for individuals facing mental health challenges, including those with chronic illnesses.
- Online Communities:
- Websites like Diabetes Daily and TuDiabetes host forums and discussions where individuals can connect, share experiences, and find support.
- Local Support Groups:
- Many communities have local support groups for individuals with diabetes. Check with local hospitals or diabetes clinics for information on available groups.
- Hotlines and Text Lines:
- National hotlines, such as the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, can offer immediate support in times of crisis.
Conclusion
The mental health impact of diabetes is significant and can affect individuals’ quality of life. By recognizing the psychological challenges, implementing effective coping strategies, and seeking support, individuals can manage both their physical and mental health more effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; resources and support systems are available to help you navigate the complexities of living with diabetes. Prioritizing mental health is just as essential as managing blood sugar levels, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling life.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology1 day ago
Diabetology1 day ago
 Diabetology1 day ago
Diabetology1 day ago