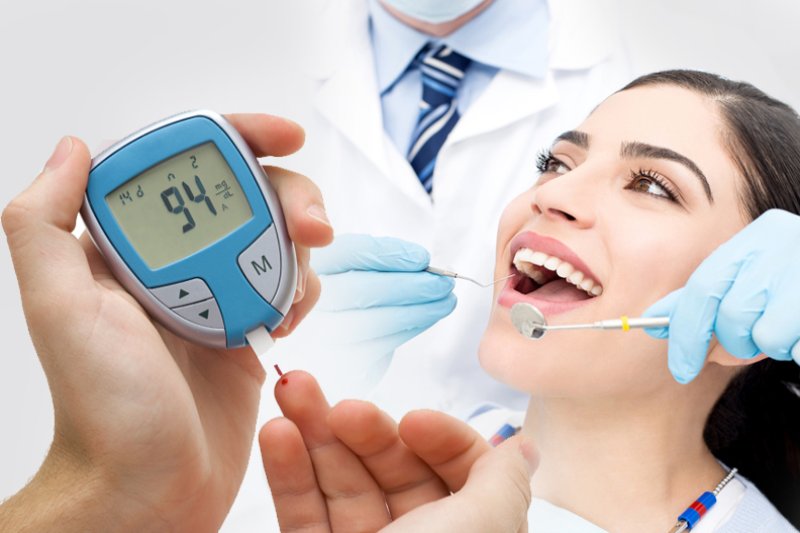
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, influencing not only blood sugar levels but also overall health. One area often overlooked in diabetes management is oral health. However, maintaining good dental care is critical for those with diabetes, as the condition can significantly impact oral health, and in turn, poor oral health can complicate diabetes management. This article explores the vital connection between dental care and diabetes, offering practical advice for maintaining a healthy mouth and managing diabetes effectively.
Understanding the Risks: How Diabetes Affects Oral Health
Diabetes increases the risk of various oral health issues, primarily due to high blood sugar levels, which can cause multiple complications in the mouth. One of the most significant concerns is periodontal disease, a severe form of gum disease that affects the tissues and bones supporting the teeth. Individuals with diabetes are more prone to infections, and their healing processes are often slower, making them more vulnerable to gum disease and other oral infections.
Another common issue for diabetics is dry mouth, known as xerostomia. Reduced saliva production can lead to a dry mouth, increasing the risk of cavities and oral infections. Saliva plays a crucial role in washing away food particles and neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, so its absence can lead to a higher prevalence of tooth decay and gum disease.
The Bidirectional Relationship: Oral Health and Blood Sugar Control
The relationship between diabetes and oral health is bidirectional. While diabetes can exacerbate oral health issues, poor oral health can also make diabetes management more challenging. For instance, gum disease can lead to increased blood sugar levels, making it harder to control diabetes. This creates a vicious cycle where each condition worsens the other, underscoring the importance of comprehensive dental care in diabetes management.
Essential Dental Care Practices for Diabetics
- Regular Dental Checkups: Regular visits to the dentist are essential for early detection and management of oral health issues. Diabetics should inform their dentist about their condition and any medications they are taking, as this information can guide the dentist in providing appropriate care.
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Brushing at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are crucial for removing plaque and preventing gum disease. An antibacterial mouthwash can also help reduce the risk of infections.
- Managing Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar levels within the target range is not only important for overall health but also for maintaining good oral health. Controlled blood sugar levels can reduce the risk of gum disease and other oral complications.
- Healthy Diet Choices: A diet low in sugars and high in fiber can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of tooth decay. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly calcium and vitamin D, are beneficial for maintaining strong teeth and bones.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of gum disease, especially in people with diabetes. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve oral health and overall diabetes management.
Conclusion
Dental care plays a crucial role in the management of diabetes. By understanding the connection between diabetes and oral health, and by adopting good dental hygiene practices, individuals with diabetes can prevent oral complications and contribute to better overall health management. Regular dental checkups, proper oral care, blood sugar management, and a healthy lifestyle are all essential components of maintaining a healthy smile while effectively managing diabetes. Remember, taking care of your mouth is an integral part of taking care of your diabetes.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago