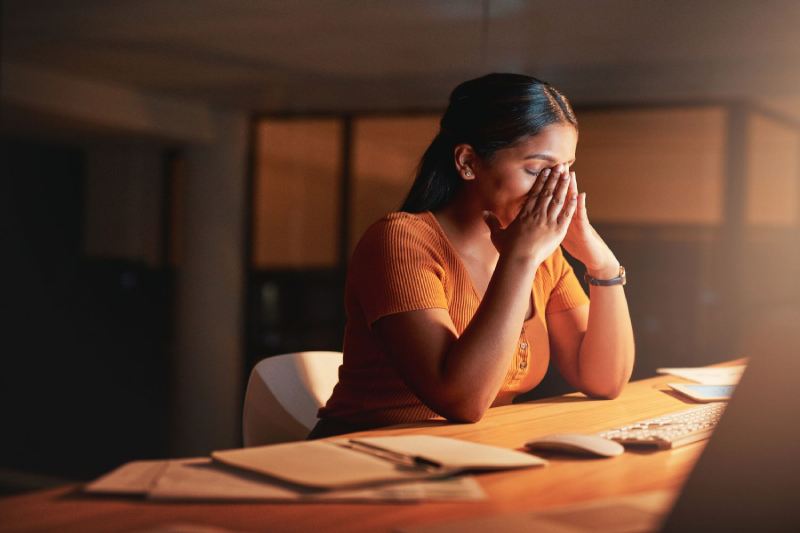
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an unwelcome companion for many. But for individuals with diabetes, chronic stress poses a significant health risk, potentially worsening blood sugar control and impacting overall well-being. This comprehensive guide delves into the complex relationship between stress and diabetes, empowering you with practical strategies to manage mental health and achieve optimal health.
Understanding Stress and the Body’s Response
Stress is a natural response to challenging or demanding situations. When you encounter stress, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones trigger a “fight-or-flight” response, preparing your body for action by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels.
While this response is crucial for short-term survival, chronic stress keeps the body in a heightened state of alert, leading to several health problems, including:
- Elevated Blood Sugar Levels: Chronically elevated stress hormones can impair insulin sensitivity, making it harder for cells to utilize glucose from the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices: Stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating sugary or processed foods, further disrupting blood sugar control.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Stress can dampen motivation for exercise, an essential element of diabetes management.
- Weakened Immune System: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, which can further complicate diabetes management.
The Two-Way Street: Diabetes and Stress
The relationship between stress and diabetes is a two-way street. Not only can stress worsen diabetes, but managing diabetes itself can be stressful. Here’s how:
- Blood Sugar Fluctuations: Managing blood sugar levels requires constant vigilance, which can be stressful. Blood sugar fluctuations, a common occurrence in diabetes, can also contribute to anxiety and mood swings.
- The Burden of Chronic Illness: Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can be emotionally draining and lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and helplessness.
- Treatment Burden: Managing medications, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adhering to dietary restrictions can feel overwhelming, contributing to stress.
Effective Strategies for Managing Stress and Diabetes
Fortunately, there are effective strategies to manage stress and improve your overall well-being:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices like meditation help promote relaxation, focus, and acceptance in the present moment. Regular meditation can be a powerful tool for managing stress and improving emotional regulation.
- Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga can effectively calm the mind and body, reducing stress response and lowering blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a potent stress reliever and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Healthy Sleep Habits: Prioritize quality sleep (7-8 hours per night) for optimal stress management and hormonal regulation.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to stress and emotional distress.
- Social Support: Building a strong support system of friends, family, or a diabetes support group can provide emotional support and a sense of community.
- Time Management: Learn effective time management skills to prioritize tasks, reduce feelings of overwhelm, and manage stress effectively.
Creating a Personalized Stress Management Plan
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to stress management. Experiment with different techniques and find what works best for you. Here are some additional tips:
- Identify Your Stress Triggers: Recognizing your personal stress triggers is crucial. Keep a journal to track situations or thoughts that typically lead to stress and develop healthy coping mechanisms to address them.
- Practice Relaxation Daily: Integrate relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises or short meditation sessions into your daily routine, even if it’s just for a few minutes.
- Disconnect to Reconnect: Schedule regular breaks from technology and social media. Spending time in nature or engaging in hobbies you enjoy can provide a sense of calm and reduce stress.
- Seek Professional Help: If stress becomes overwhelming or significantly impacts your diabetes management, don’t hesitate to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor.
Living Well with Diabetes: A Holistic Approach
Managing diabetes effectively requires a holistic approach that addresses not only blood sugar control but also mental and emotional well-being. By prioritizing stress management techniques, you empower yourself to thrive with diabetes and experience improved overall health and quality of life.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or a mental health professional before implementing any new stress management techniques or seeking support for stress-related issues.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago










