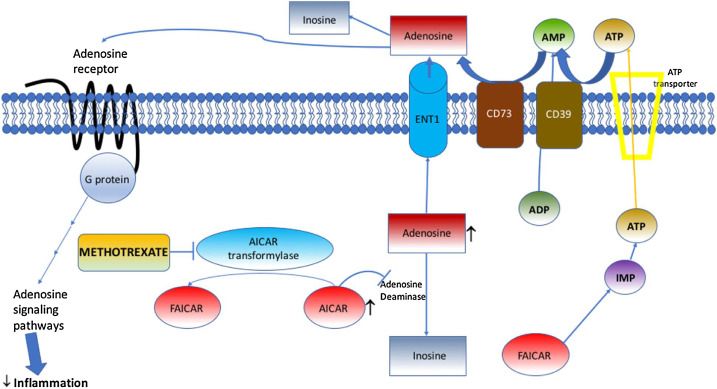
For rheumatoid arthritis that does not respond to methotrexate to the maximum tolerated dose, the combination of anti-TNF and methotrexate is effective. However, it is unclear what the best dose of methotrexate to take once under anti-TNF treatment is.
According to a study that was published in The Lancet Rheumatology, combining methotrexate with an anti-TNF makes it possible to reduce the dosage to approximately 10 mg per week without sacrificing efficacy or experiencing fewer adverse effects.
Same rates of remission
291 of the 300 patients who were recruited were analyzed. 105 patients entered remission at week 24 and continued methotrexate monotherapy until week 48. One hundred and 34 patients didn’t accomplish reduction at week 24 and were randomized to get adalimumab in addition to the greatest endured portion of methotrexate (n=68) or adalimumab in addition to a diminished dose of methotrexate (n=66).
25 (38%) of the 66 patients and 27 (44%) of the 61 patients went into remission at week 48, respectively, with an adjusted risk difference of 6.4 (90% CI -7.0 to 19.8), which is the non-inferiority margin of -15 percent.
After week 24, adverse events were more likely to occur in the group taking the maximum tolerated dose of methotrexate than in the group taking a lower dose (24 [35%] versus 13 [20%], p=0-054).
A two-dose randomized trial of methotrexate against TNF
Patients who had rheumatoid arthritis for less than two years were recruited for this open-label randomized controlled MIRACLE trial from 24 secondary or tertiary care hospitals in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. Oral methotrexate was taken by the patients six to eight mg per week. At week 12, the maximum tolerated dose was increased to ten and twenty-five mg per week.
Adalimumab with a maximum tolerated dose of methotrexate ( 25 mg/wk) or a reduced dose of methotrexate (6 to 8 mg/wk) was randomized to patients who did not achieve remission.
There is no need to take a lot of methotrexate
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis whose response to methotrexate monotherapy was insufficient, the MIRACLE study demonstrates that adalimumab plus a reduced dose of methotrexate is not less effective than adalimumab plus a maximum dose of methotrexate.
The group taking methotrexate at a lower dose experiences fewer adverse events. This indicates that these patients can safely reduce their methotrexate dosage.

 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology7 days ago
Diabetology7 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago