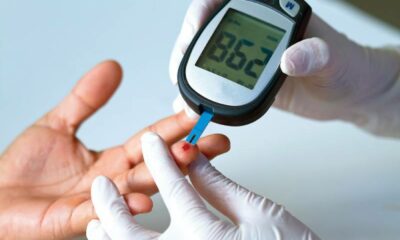
Diabetes and heart disease often go hand in hand, as diabetes can significantly increase the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial, but it’s also essential to focus on heart health to reduce the risk of heart disease. This article explores effective strategies for diabetics to lower their heart disease risk and maintain overall cardiovascular health.
Understanding the Diabetes-Heart Disease Connection
Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is a major risk factor for heart disease. High blood sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in the arteries), which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, diabetes often comes with other risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity.
Key Strategies to Reduce Heart Disease Risk
1. Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining optimal blood sugar control is critical for reducing heart disease risk. Consistent blood sugar levels help prevent damage to blood vessels and nerves. Regular monitoring, adhering to a diabetes-friendly diet, and following prescribed medications or insulin therapy are essential for effective blood sugar management.
Tips:
- Monitor blood glucose levels regularly.
- Work with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- Use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) if recommended by your doctor.
2. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
A balanced diet plays a significant role in managing both diabetes and heart disease. Focus on foods that support heart health, such as:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: High in fiber and can help control blood sugar levels.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for fish, poultry, and plant-based proteins.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, while limiting saturated and trans fats.
Tips:
- Limit intake of refined carbohydrates and sugary foods.
- Choose low-sodium options to manage blood pressure.
- Monitor portion sizes to maintain a healthy weight.
3. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing diabetes and reducing heart disease risk. It helps improve blood circulation, lowers blood sugar levels, and strengthens the heart. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Tips:
- Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Choose activities you enjoy to stay motivated.
- Consult your doctor before starting a new exercise regimen, especially if you have existing health concerns.
4. Monitor and Manage Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a common issue in diabetics and a significant risk factor for heart disease. Regularly monitor your blood pressure and work with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing salt intake, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications, can help keep blood pressure in check.
Tips:
- Check blood pressure regularly and track readings.
- Reduce sodium intake by cooking at home and avoiding processed foods.
- Incorporate stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga.
5. Control Cholesterol Levels
Diabetes often affects cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Aim to maintain healthy levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and increase HDL (good) cholesterol through diet and medication if needed. Foods high in soluble fiber, like oats and beans, can help lower LDL cholesterol.
Tips:
- Include heart-healthy foods like nuts, fish, and legumes in your diet.
- Limit intake of high-cholesterol foods such as fatty meats and full-fat dairy products.
- Follow your doctor’s advice regarding cholesterol-lowering medications.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can exacerbate diabetes and increase heart disease risk. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise is crucial for heart health.
Tips:
- Set realistic weight loss goals and track progress.
- Focus on gradual, sustainable changes in diet and activity levels.
- Seek support from a dietitian or weight management program if needed.
7. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol intake can significantly increase heart disease risk. If you smoke, seek support to quit, and limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels—no more than one drink per day for women and two for men.
Tips:
- Utilize smoking cessation programs or therapies.
- Choose healthier coping mechanisms for stress and social situations.
- Monitor alcohol intake and consider non-alcoholic alternatives.
Conclusion
Reducing heart disease risk is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes. By focusing on blood sugar control, adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding harmful habits, diabetics can significantly lower their risk of cardiovascular complications. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider will help you stay on track and make necessary adjustments to your management plan.
Prioritizing these strategies can lead to better heart health and overall well-being, empowering diabetics to live healthier, longer lives.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago