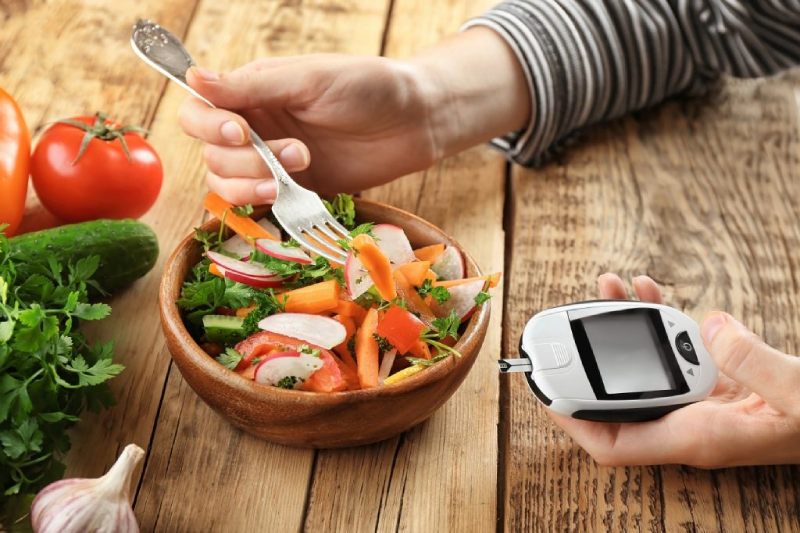
Managing blood sugar levels is a crucial part of living with diabetes, and one of the most effective ways to do so is by incorporating low glycemic index (GI) foods into your diet. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after consumption. Foods with a low GI value (55 or below) cause a slower and more controlled rise in blood sugar, making them an excellent choice for those with diabetes or anyone looking to maintain stable energy levels throughout the day. Let’s dive into the benefits and examples of low glycemic foods you can include in your meals.
What is the Glycemic Index?
The glycemic index is a ranking of foods based on how they impact blood sugar levels. Foods that are high on the GI scale (70 or more) cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, while those with a low GI (55 or below) release glucose more slowly, helping to prevent spikes and crashes.
Benefits of Low Glycemic Index Foods
- Improved Blood Sugar Control
Low GI foods help stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing sudden spikes and drops that can lead to symptoms like fatigue, irritability, and hunger.
- Better Weight Management
These foods tend to be more filling, making it easier to control hunger and prevent overeating, which is key for managing weight.
- Reduced Risk of Heart Disease
Studies suggest that a diet rich in low GI foods can reduce the risk of heart disease, which is a common complication of diabetes.
- Increased Energy
By providing a steady and gradual release of glucose, low GI foods help sustain energy levels throughout the day.
Top Low Glycemic Index Foods to Include in Your Diet
- Non-Starchy Vegetables
Leafy greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, and bell peppers are all low in carbs and have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. They’re also packed with essential vitamins and minerals.
- Whole Grains
Whole grains like quinoa, barley, and oats have a lower GI than refined grains. These foods provide fiber, which slows down digestion and helps regulate blood sugar.
- Legumes and Beans
Lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, and black beans are great sources of plant-based protein and fiber. They have a low GI and provide long-lasting energy.
- Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are low-GI snacks that are also rich in healthy fats, fiber, and protein, helping to manage blood sugar effectively.
- Fruits
Certain fruits like berries, apples, and pears are low-GI and full of antioxidants and fiber. However, it’s important to monitor portion sizes, as some fruits may have a moderate GI.
- Dairy
Milk and yogurt (especially unsweetened) have a low glycemic index, providing a good source of calcium and protein.
How to Incorporate Low Glycemic Foods into Your Diet
- Start with Breakfast: Begin your day with a bowl of steel-cut oats, topped with berries and chia seeds, or a vegetable omelet with avocado.
- Snack Smart: Choose snacks like a handful of almonds, a small apple, or carrot sticks with hummus.
- Make Smart Substitutions: Replace white rice with quinoa or brown rice, and switch from white bread to whole-grain or sprouted bread.
- Combine Foods: Pair higher-GI foods with low-GI options to help moderate the overall blood sugar impact of your meal. For example, combine a baked potato (higher GI) with a salad or protein-rich food (both low GI).
Conclusion
Incorporating low glycemic index foods into your diet is a powerful tool for managing blood sugar levels, whether you’re dealing with diabetes or aiming for better overall health. These foods provide steady energy, help control cravings, and can even reduce the risk of heart disease. Always work with a healthcare professional or dietitian to tailor your meals to your specific needs, but starting with low-GI foods is a great way to build a more balanced and diabetes-friendly diet.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago











