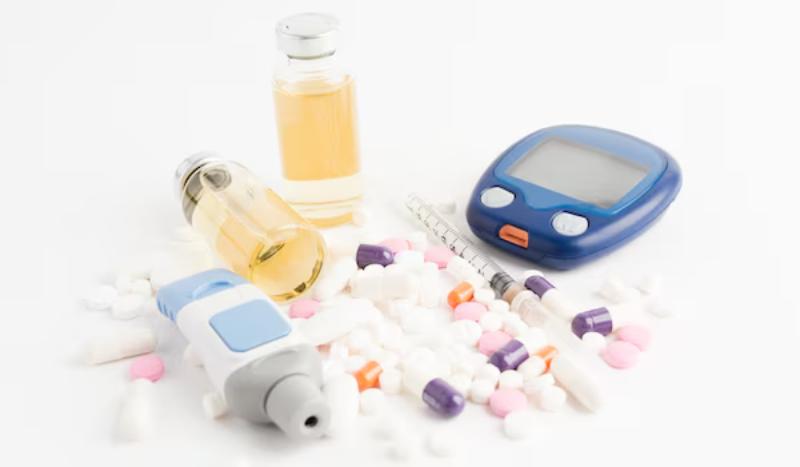
Managing diabetes often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. For many with Type 2 diabetes, oral medications are a vital tool in keeping blood sugar levels under control. These medications work in various ways to regulate glucose levels and improve overall health. Here’s an in-depth look at how they function and the role they play in diabetes management.
Understanding Blood Sugar and Insulin
- Briefly explain how blood sugar levels are regulated in the body.
- Highlight the role of insulin in managing glucose and what happens in Type 2 diabetes (e.g., insulin resistance, reduced insulin production).
Types of Oral Diabetes Medications
a. Biguanides (e.g., Metformin)
- Explain how they reduce glucose production in the liver.
- Highlight their ability to improve insulin sensitivity.
b. Sulfonylureas
- Discuss how these stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
c. Meglitinides
- Similar to sulfonylureas but with a shorter action span, ideal for post-meal blood sugar control.
d. DPP-4 Inhibitors
- Explain their role in increasing insulin release and reducing glucose production by inhibiting the DPP-4 enzyme.
e. SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Highlight their unique mechanism of removing excess glucose through urine.
f. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
- Discuss how they improve insulin sensitivity in fat and muscle cells.
g. Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- Describe how they slow the breakdown of carbohydrates in the intestines, reducing post-meal blood sugar spikes.
How These Medications Work Together
- Explain that some people may require a combination of medications to target different aspects of blood sugar control.
- Mention how physicians tailor treatment plans based on individual needs and health conditions.
Benefits of Oral Diabetes Medications
- Improved blood sugar control.
- Convenience compared to injections (in many cases).
- Prevention of long-term complications, such as heart disease or nerve damage.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
- Mention common side effects like nausea, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), or weight gain with some medications.
- Stress the importance of regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers.
Complementary Lifestyle Changes
- Highlight the role of diet, exercise, and weight management in enhancing the effectiveness of oral diabetes medications.
- Emphasize that medication is just one part of a comprehensive diabetes management plan.
Conclusion
Oral diabetes medications are a powerful tool in controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications. By understanding how these medications work, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve better health outcomes.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology19 hours ago
Diabetology19 hours ago