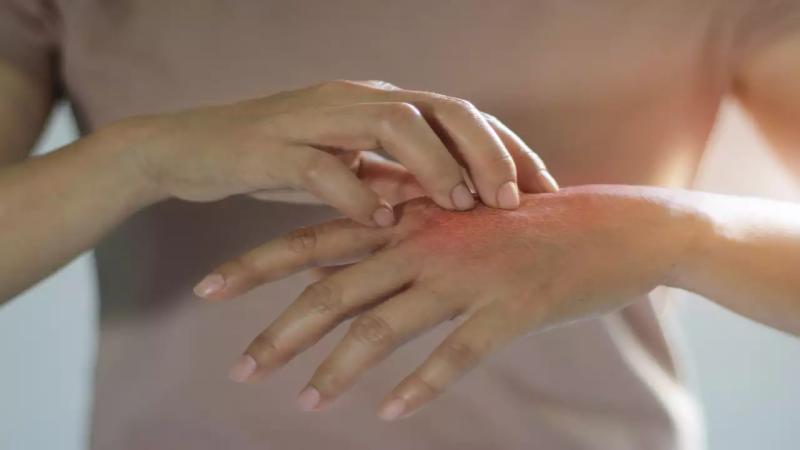
Diabetes can have a significant impact on your skin health due to fluctuating blood sugar levels and the body’s ability to heal itself. Managing diabetes effectively can reduce the risk of skin problems, but it’s important to understand the specific ways in which the condition can affect the skin and how to care for it.
1. Dry Skin
High blood sugar levels can lead to dehydration, which makes the skin dry, flaky, and prone to irritation. The body’s inability to regulate moisture properly can cause the skin to become rough and cracked, especially on the feet, hands, and legs.
How to Care for It:
- Moisturize regularly using a thick, fragrance-free cream or lotion.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Avoid hot showers, as they can dry out the skin further.
- Choose mild, gentle soaps and body washes that don’t strip the skin of natural oils.
2. Itchy Skin
Itching is a common skin issue for people with diabetes. Dryness and poor circulation can make the skin more prone to irritation. Additionally, high blood sugar can increase the risk of yeast infections and fungal growth, leading to itchy skin, especially in areas like the groin, underarms, or between toes.
How to Care for It:
- Apply anti-itch creams or hydrocortisone to affected areas as recommended by your doctor.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to prevent irritation.
- Ensure your blood sugar is within the target range to prevent skin dryness and other complications.
3. Infections
People with diabetes are more vulnerable to skin infections due to impaired circulation and a weakened immune system. Common infections include bacterial infections (like styes or boils) and fungal infections (such as athlete’s foot or yeast infections). High blood sugar can also slow down the healing process.
How to Care for It:
- Keep your skin clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Treat cuts and scrapes immediately with an antiseptic and keep the area covered.
- Monitor wounds regularly for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain.
4. Delayed Wound Healing
Diabetics often experience delayed wound healing due to poor circulation and high blood glucose levels. Small cuts, blisters, or abrasions can take longer to heal, increasing the risk of infections and other complications.
How to Care for It:
- Keep your wounds clean and covered with sterile bandages.
- Ensure your blood sugar levels are well-controlled to promote faster healing.
- If a wound isn’t healing, seek medical attention to prevent further complications.
5. Skin Discoloration
High blood sugar levels can cause a condition called diabetic dermopathy, which results in brown, scaly patches on the skin, usually on the shins. These patches are non-itchy and usually harmless, but they can be a sign of poor blood sugar control.
How to Care for It:
- Keep your blood sugar levels stable to reduce the appearance of dermopathy.
- Moisturize the affected areas to prevent excessive dryness and irritation.
6. Blisters
Some people with diabetes may develop blisters, especially on their hands, feet, and lower legs. These blisters often appear without injury and are typically filled with clear fluid. They are more common in individuals with poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
How to Care for It:
- Avoid popping blisters to prevent infection.
- Keep the blistered area clean and covered.
- Check your blood sugar regularly to help prevent the formation of blisters.
7. Darkened Skin (Acanthosis Nigricans)
Acanthosis nigricans is a condition that causes dark, velvety patches to form on the skin, typically around the neck, armpits, or groin. It is often a sign of insulin resistance, a common feature of type 2 diabetes.
How to Care for It:
- Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly to manage insulin resistance.
- Consult your doctor to determine if any treatments, such as topical creams, can help lighten the darkened areas.
- General Skin Care Tips for Diabetics:
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to reduce the risk of skin complications.
- Practice good hygiene by bathing regularly but avoiding harsh soaps or hot water, which can strip the skin of moisture.
- Inspect your skin daily for any signs of cuts, blisters, or infections, especially on your feet.
- Use sunscreen daily to protect your skin from UV damage, as diabetes can make the skin more susceptible to sunburn.
- Manage stress as it can negatively affect blood sugar levels and, consequently, your skin health.
- By understanding how diabetes affects the skin and incorporating proper skincare practices, you can help prevent common skin issues and keep your skin healthy. If you notice any unusual changes in your skin, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized care and treatment options.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago





