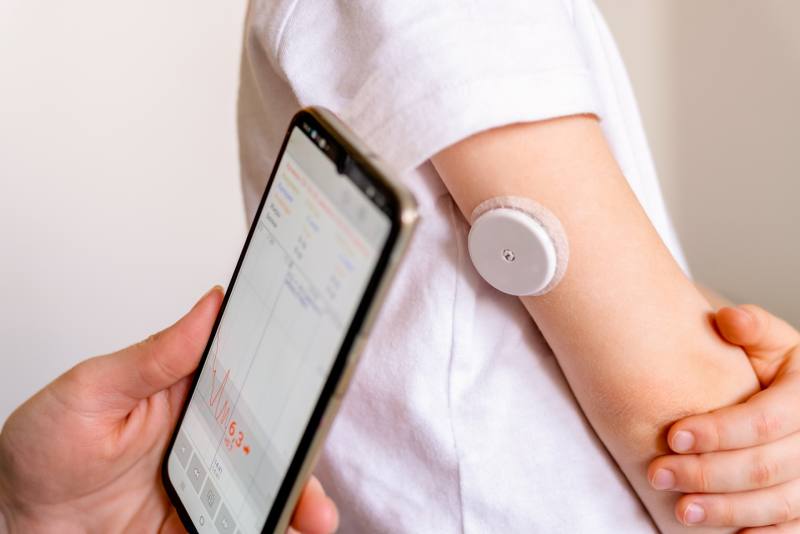
In recent years, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices have revolutionized the management of Type 1 diabetes, offering a more precise and convenient approach to controlling blood sugar levels. These small, wearable devices track glucose levels in real time, providing critical insights that were previously only available through periodic finger-prick tests. The real-time data and alerts offered by CGMs are helping people with Type 1 diabetes take proactive steps to manage their condition more effectively.
Real-Time Monitoring for Better Control
Unlike traditional glucose monitoring, which requires intermittent blood checks, CGM devices provide a continuous stream of glucose data throughout the day and night. This allows for the detection of patterns and trends that might otherwise be missed, such as rapid spikes or dips in glucose levels. With this detailed data, people with Type 1 diabetes can make informed decisions about insulin dosing, diet, and exercise, helping to prevent dangerous highs (hyperglycemia) and lows (hypoglycemia).
Reducing the Burden of Diabetes Management
For many, the constant need for blood sugar checks and insulin adjustments can feel overwhelming. CGMs have made diabetes management less invasive and more seamless. These devices send glucose readings directly to a smartphone or smartwatch, allowing users to track their glucose without the need for painful finger-prick tests. Many CGM systems also alert users to potential issues, such as when their glucose is about to rise or fall outside the target range, enabling faster responses.
Improved Outcomes and Quality of Life
Studies have shown that using CGMs leads to better glycemic control, reducing HbA1c levels and the risk of complications associated with long-term high blood sugar. For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, tighter glucose control can reduce the risk of kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve damage. Additionally, CGMs can help individuals maintain a more stable glucose level, improving energy levels and overall well-being.
Integration with Insulin Pumps for Advanced Care
Some of the most advanced CGM systems now integrate with insulin pumps, creating hybrid closed-loop systems, sometimes referred to as artificial pancreas technology. These systems automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, reducing the need for manual adjustments and offering a more automated approach to diabetes care. This combination of technologies is transforming diabetes management, offering more freedom and flexibility to users.
Future Innovations in CGM Technology
As technology continues to evolve, CGM devices are becoming smaller, more accurate, and even less invasive. Future innovations may include longer sensor life, non-invasive options that don’t require skin insertion, and greater integration with artificial intelligence to predict glucose trends and suggest more personalized treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Continuous glucose monitoring devices are more than just a convenience; they represent a significant leap forward in Type 1 diabetes care. By providing real-time data, reducing the need for frequent finger-pricks, and integrating with other advanced diabetes technologies, CGMs are empowering individuals to take greater control over their health and improving both immediate outcomes and long-term quality of life. As these devices continue to evolve, the future of diabetes care looks more promising than ever.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 day ago
Diabetology1 day ago
 Diabetology12 hours ago
Diabetology12 hours ago
 Diabetology12 hours ago
Diabetology12 hours ago