Ramadan is a sacred time for millions of Muslims around the world, marked by fasting from dawn to dusk. However, for individuals with diabetes, fasting can pose unique health challenges. Managing blood sugar levels while observing fasts requires careful planning and medical guidance to avoid complications like hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
If you have diabetes and plan to fast, this guide will help you make informed decisions to ensure a safe and healthy Ramadan.
1. Consult Your Doctor Before Fasting
Before deciding to fast, consult your doctor or diabetes specialist. They can assess your health condition, adjust medications if necessary, and provide personalized advice based on your diabetes type and overall health.
Who Should Avoid Fasting?
- Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes.
- Those with a history of severe hypoglycemia or ketoacidosis.
- Pregnant women with diabetes.
- People with diabetes-related complications, such as kidney or heart disease.
If your doctor advises against fasting, consider alternative ways to participate in Ramadan, such as charity or additional prayers.
2. Plan Your Meals for Suhoor and Iftar
Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels during fasting depends on eating the right foods at Suhoor (pre-dawn meal) and Iftar (breaking the fast).
Suhoor: The Pre-Dawn Meal
- Eating a nutritious and slow-digesting meal at Suhoor can help sustain energy levels throughout the day. Include:
- High-fiber foods: Whole grains, oats, legumes, and vegetables.
- Healthy proteins: Eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and nuts.
- Good fats: Avocados, olive oil, and nuts.
- Hydration: Plenty of water and herbal teas.
Avoid: Sugary cereals, processed foods, and excessive caffeine, as they can cause dehydration and blood sugar spikes.
Iftar: Breaking the Fast
- Iftar should be a balanced meal to restore energy without causing rapid blood sugar fluctuations. Recommended foods include:
- Dates (in moderation) for natural energy.
- Lean proteins like grilled chicken, fish, or tofu.
- Healthy carbohydrates such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread.
- Plenty of vegetables and healthy fats.
Avoid: Fried foods, sugary drinks, and excessive sweets, as they can lead to blood sugar spikes.
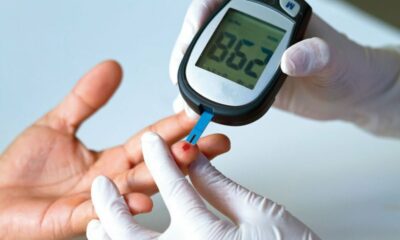
3. Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is crucial while fasting. Check your levels:
- Before Suhoor and Iftar.
- During the day, especially if you feel dizzy, weak, or excessively thirsty.
- Two hours after breaking the fast to assess post-meal glucose levels.
If your blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL or rises above 300 mg/dL, break your fast immediately and seek medical advice.
4. Adjust Your Medications and Insulin
Fasting can alter how your body processes medications, including insulin. Work with your doctor to adjust:
- Oral medications: Some may need dosage changes.
- Insulin therapy: Long-acting insulin may be preferred to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Never stop or modify your medication without consulting a healthcare provider.
5. Stay Hydrated and Avoid Overeating
- Drink 8–10 glasses of water between Iftar and Suhoor to prevent dehydration.
- Limit caffeinated drinks, as they can cause fluid loss.
- Eat moderate portions to prevent post-meal hyperglycemia.
6. Engage in Safe Physical Activity
- Light activities like walking after Iftar can help regulate blood sugar.
- Avoid intense workouts while fasting, as they may cause hypoglycemia.
- The best time for exercise is after Iftar when energy levels are replenished.
7. Recognize Warning Signs and When to Break Your Fast
If you experience any of the following symptoms, break your fast immediately and seek medical help:
Dizziness, confusion, or excessive fatigue.
Severe thirst, nausea, or vomiting.
Blurred vision or rapid heartbeat.
Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL or above 300 mg/dL.
Conclusion
Fasting with diabetes is possible with proper planning and medical supervision. Prioritizing balanced meals, hydration, and regular blood sugar monitoring can help ensure a safe and spiritually fulfilling Ramadan. Always listen to your body and consult a healthcare professional if you experience any complications.
By taking these precautions, you can observe Ramadan safely while maintaining good diabetes management.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago