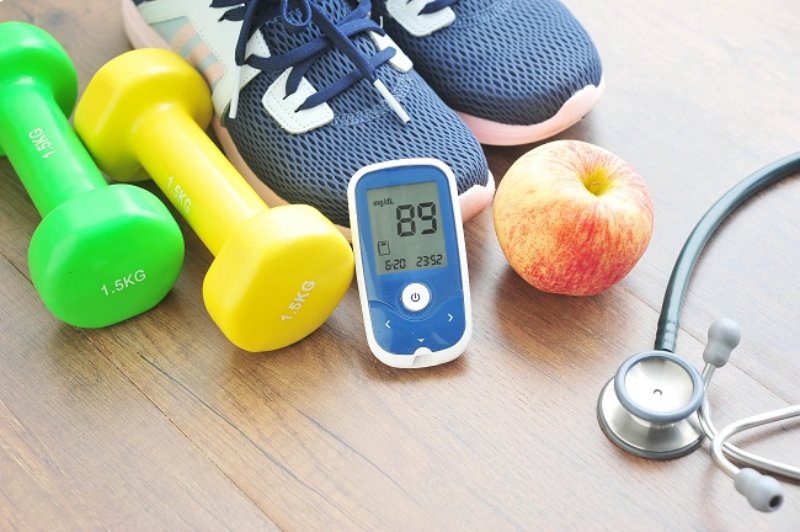
For individuals living with diabetes, maintaining optimal health is a multifaceted endeavor that includes medication, diet, and regular physical activity. Exercise is particularly important as it helps regulate blood sugar levels, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts overall well-being. This article explores the best physical activities for diabetics to help them achieve and maintain optimal health.
Understanding the Importance of Exercise for Diabetics
Exercise plays a vital role in diabetes management for several reasons:
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Physical activity helps muscles absorb glucose more efficiently, reducing the need for insulin.
- Controls Blood Sugar Levels: Regular exercise can help lower blood glucose levels and prevent spikes.
- Aids in Weight Management: Helps in maintaining a healthy weight, which is crucial for diabetes management.
- Boosts Cardiovascular Health: Reduces the risk of heart disease, a common complication of diabetes.
- Enhances Mental Health: Releases endorphins that improve mood and reduce stress.
Aerobic Exercises
Aerobic exercises, also known as cardio, are activities that increase your heart rate and breathing. They are effective in improving cardiovascular health and managing blood sugar levels.
- Walking:
- Benefits: Easy to incorporate into daily routine, low impact, and requires no special equipment.
- Recommendation: Aim for at least 30 minutes of brisk walking most days of the week.
- Cycling:
- Benefits: Low-impact exercise that is gentle on the joints, can be done indoors or outdoors.
- Recommendation: Ride a bike for 30-60 minutes, 3-5 times a week.
- Swimming:
- Benefits: Full-body workout that is easy on the joints, improves cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength.
- Recommendation: Swim laps for 30-60 minutes, 3-5 times a week.
- Running or Jogging:
- Benefits: High-impact exercise that burns more calories, improves cardiovascular endurance.
- Recommendation: Run or jog for 20-30 minutes, 3-5 times a week, starting with shorter durations and gradually increasing.
Strength Training
Strength training helps build muscle mass, which improves glucose uptake and increases metabolism.
- Weight Lifting:
- Benefits: Increases muscle mass and strength, boosts metabolic rate.
- Recommendation: Perform weight lifting exercises 2-3 times a week, targeting all major muscle groups.
- Resistance Band Exercises:
- Benefits: Portable and versatile, suitable for various fitness levels.
- Recommendation: Use resistance bands for exercises like squats, rows, and chest presses, 2-3 times a week.
- Bodyweight Exercises:
- Benefits: No equipment needed, can be done anywhere.
- Recommendation: Include exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, squats, and planks in your routine, 2-3 times a week.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Flexibility and balance exercises are important for maintaining joint health and preventing injuries.
- Yoga:
- Benefits: Improves flexibility, strength, and mental well-being.
- Recommendation: Practice yoga 2-3 times a week, focusing on poses that stretch and strengthen various muscle groups.
- Pilates:
- Benefits: Enhances core strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Recommendation: Attend Pilates classes or follow online routines 2-3 times a week.
- Tai Chi:
- Benefits: Low-impact exercise that improves balance, flexibility, and reduces stress.
- Recommendation: Practice Tai Chi 2-3 times a week.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. It is effective for improving cardiovascular fitness and insulin sensitivity.
- HIIT Workouts:
- Benefits: Efficient calorie burning, improves cardiovascular and metabolic health.
- Recommendation: Incorporate HIIT workouts 1-2 times a week, starting with shorter durations and gradually increasing intensity.
Daily Activity and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to structured workouts, increasing overall daily activity can significantly impact blood sugar control and overall health.
- Active Commuting:
- Benefits: Increases daily physical activity.
- Recommendation: Walk or bike to work or school whenever possible.
- Household Chores:
- Benefits: Keeps you active throughout the day.
- Recommendation: Engage in activities like gardening, cleaning, and yard work regularly.
- Taking the Stairs:
- Benefits: Boosts cardiovascular health and leg strength.
- Recommendation: Opt for stairs over elevators and escalators whenever possible.
Monitoring and Adjusting Exercise Routines
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise is crucial for diabetics. This helps in understanding how different activities affect blood sugar and allows for necessary adjustments.
- Keep a Log: Record your workouts, blood sugar levels, and any symptoms to identify patterns and make informed adjustments.
- Hypoglycemia Awareness: Be aware of signs of low blood sugar (dizziness, sweating, confusion) and carry fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets or fruit juice.
- Adjust Insulin and Medication: Consult your doctor about adjusting insulin or medication doses based on your exercise routine.
Conclusion
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing diabetes and improving overall health. By incorporating a mix of aerobic, strength, flexibility, and HIIT exercises, diabetics can achieve better blood sugar control, enhanced fitness, and a higher quality of life. Remember to consult healthcare providers, monitor blood sugar levels, and make gradual adjustments to find the most effective workout routine for your needs.

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 day ago
Diabetology1 day ago
 Diabetology13 hours ago
Diabetology13 hours ago
 Diabetology13 hours ago
Diabetology13 hours ago