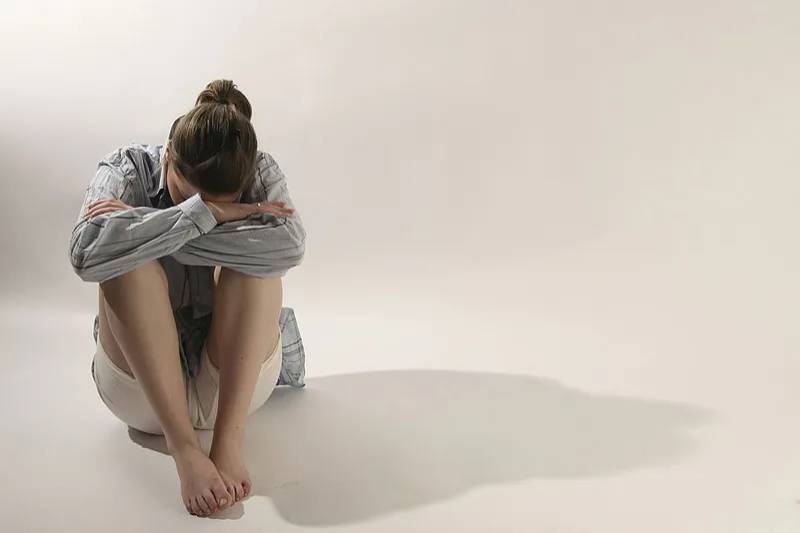
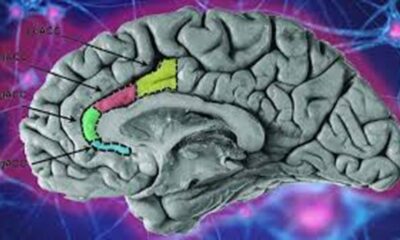
Addiction, depression, chronic pain, and suicide risk are all linked and have a significant effect on mental health. The relationship between these variables emphasizes how crucial it is to identify the warning indicators connected to each illness and to take proactive measures to properly manage these conditions. In this piece, we examine these problems in further detail, examine how they relate to one another, and offer helpful suggestions for overcoming these difficulties.
Depression and Its Effects
A frequent mental ailment that affects millions of individuals worldwide is depression. A confluence of environmental, psychological, and biological variables cause it to occur. Not only can depression present psychologically, but it can also manifest physically and behaviorally, resulting in symptoms including insomnia, changes in appetite, and chronic fatigue. Withdrawing from one’s social support system as a result of this illness might exacerbate feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Nonetheless, a variety of coping mechanisms can be used to effectively treat depression. These include of mindfulness and relaxation practices, medicine, therapy, stress reduction, and positive lifestyle adjustments. It is vital to recognize that each person’s experience with depression is distinct, necessitating the customization of coping mechanisms to suit their distinctive requirements and situations.
Problems with Substance dependency and Addiction
Addiction, often known as substance use disorder, is a serious problem that is intimately related to mental health issues including depression. Similar to depression, a mix of biological, psychological, and environmental variables can lead to addiction. Addiction can have both behavioral and physical symptoms, and it’s important to identify these early on in order to get treatment in a timely manner.
Though it might be difficult, talking to a loved one about their addiction is a crucial first step on the road to recovery. Behavioral health and mental health services play a crucial role in this context because they offer addicts the support and guidance they need to overcome their addiction and begin the process of healing.
Risk of Suicide and Prevention
Addiction, severe pain, and untreated mental health concerns all tragically lead to suicide. Experts in mental health have identified a number of risk factors for suicide, such as substance addiction, mental illnesses, major life losses, and excruciating physical or emotional suffering. Reducing access to suicide tools, treating mental illnesses and substance misuse, and enhancing general quality of life are all important components of suicide prevention initiatives.
The COVID-19 epidemic has made the mental health issue worse and raised the risk of suicide, self-harm, sadness, and anxiety. It’s critical for prevention to recognize the warning signs of suicide, which include changes in behavior, mood, or sleep patterns; social disengagement; or talking about death or suicide.
In summary, the intricate relationship among depression, chronic pain, addiction, and suicide risk must be addressed immediately. Improving the outcomes of mental health can be greatly aided by being aware of the warning signs connected with each disorder and by taking preventative action. Recall that seeking assistance is the first step toward healing and that mental health is just as vital as physical health.
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago