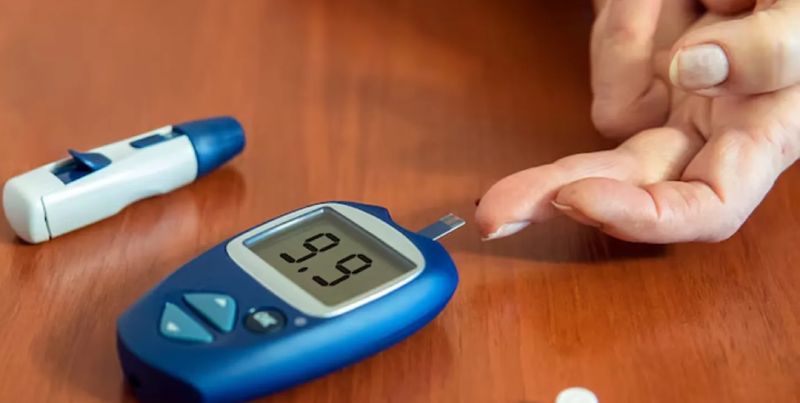
Diabetes is a growing global health issue, with millions of people at risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices are often the primary cause of the disease. The good news is that diabetes is preventable with the right knowledge and habits. This article will highlight the early warning signs of diabetes and provide effective lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Early Warning Signs of Diabetes
Many people develop diabetes gradually over time without noticing the subtle changes in their body. Identifying the early signs can help take preventive action before the condition becomes chronic.
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
One of the most common early signs of diabetes is frequent urination, especially at night. Elevated blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb the excess sugar, leading to increased urination.
2. Increased Thirst (Polydipsia)
As the body loses more water due to frequent urination, dehydration sets in, causing persistent thirst. Drinking more water than usual may be an indication of elevated blood sugar levels.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Sudden, unintentional weight loss can be a sign of diabetes. The body starts breaking down muscle and fat for energy when it can’t access glucose properly, leading to weight loss despite increased hunger or eating.
4. Fatigue and Weakness
High blood sugar levels interfere with the body’s ability to use glucose for energy. This can result in constant tiredness, even if you are well-rested.
5. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar can cause swelling in the eye’s lens, resulting in blurred vision. If untreated, prolonged high blood sugar levels can cause permanent damage to the eyes.
6. Slow-Healing Wounds
Diabetes impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds, especially on the feet. If cuts, bruises, or sores are slow to heal, it could be an early sign of diabetes.
7. Numbness or Tingling in Hands and Feet
Prolonged high blood sugar can damage nerves, leading to a tingling or numb sensation in your hands or feet. This condition, known as diabetic neuropathy, can be a sign of prediabetes or diabetes.
8. Increased Hunger (Polyphagia)
Despite eating regularly, feeling constantly hungry may indicate that your body isn’t properly using glucose for energy. This symptom is often paired with fatigue and weight loss.
Effective Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Diabetes
Making changes in your daily habits can drastically reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Here are the most effective lifestyle changes to consider:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in preventing diabetes. Focus on eating nutrient-dense foods that help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
- Choose Whole Grains: Replace refined carbohydrates with whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats. Whole grains are high in fiber, which helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
- Eat Plenty of Fiber: High-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains improve blood sugar control. Fiber helps you feel full, prevents overeating, and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Limit Sugary Foods and Beverages: Sugary snacks, desserts, and soft drinks cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. Opt for healthier alternatives like fruit and water to avoid these surges.
- Prioritize Lean Proteins and Healthy Fats: Including sources of lean protein such as chicken, fish, and plant-based proteins (like tofu or legumes) and healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil) can stabilize blood sugar levels.
2. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to use glucose more effectively. Even modest amounts of exercise can reduce your risk of diabetes.
- Aim for at Least 150 Minutes per Week: Moderate-intensity exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling for 30 minutes a day, five times a week can lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Incorporate Strength Training: Resistance training or lifting weights 2–3 times per week can improve muscle mass and increase the body’s ability to use glucose.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight, especially carrying excess fat around the abdomen, increases the risk of insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Losing even a small percentage of body weight (5–10%) can significantly reduce your diabetes risk.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes by 30-40%. Quitting smoking improves your insulin sensitivity, reduces inflammation, and lowers your risk of heart disease and other diabetes complications.
5. Limit Alcohol Intake
Excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain, both of which elevate the risk of diabetes. Moderation is key—stick to recommended limits (no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men).
6. Get Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep or sleep deprivation increases the risk of insulin resistance, which can lead to Type 2 diabetes. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night to help regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
7. Manage Stress
Chronic stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood sugar levels. Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies to manage your stress levels effectively.
Regular Health Checkups and Monitoring
1. Know Your Risk Factors
Certain factors increase your risk of developing diabetes. These include family history, age (over 45), a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and high blood pressure. If you fall into one or more of these categories, it’s important to take extra precautions.
2. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
For those at risk of developing diabetes, regularly monitoring blood sugar levels can provide early insight into any irregularities. A healthcare professional can conduct a fasting blood sugar test or A1C test to assess your average blood sugar levels over time.
3. Get Regular Health Screenings
Routine checkups with your doctor, especially if you are overweight or have a family history of diabetes, can help catch early signs of prediabetes. Early detection allows you to take preventive measures before diabetes fully develops.
Preventing Prediabetes from Progressing
If you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes (elevated blood sugar levels but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis), it’s important to take action immediately to prevent progression to Type 2 diabetes. The lifestyle changes discussed in this article are particularly beneficial for reversing prediabetes.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
Diabetes prevention is within your control, and the key lies in understanding the early warning signs and adopting healthy lifestyle habits. By eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, you can reduce your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Being proactive and vigilant about your health now can make all the difference in the future.

 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago














