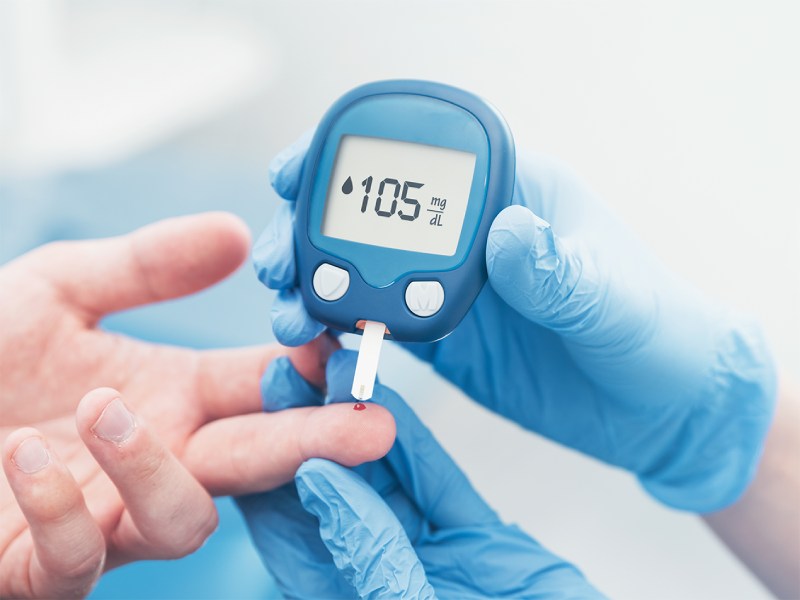
Living with diabetes involves more than just managing blood sugar levels—it also demands attention to emotional well-being. The daily routine of monitoring blood glucose, medication adherence, and dietary restrictions can lead to stress, anxiety, and even depression. Emotional health is often overlooked in diabetes care, yet it plays a crucial role in overall wellness and disease management.
Understanding the Emotional Impact of Diabetes
For many diabetics, the reality of a lifelong condition can trigger a range of emotions, from fear and frustration to guilt and sadness. Feelings of being overwhelmed by the need for constant vigilance or the unpredictability of blood sugar levels can lead to emotional burnout. Additionally, concerns about potential complications can heighten anxiety, while social stigma surrounding the disease may impact self-esteem.
Acknowledging and addressing these emotional challenges is essential to living well with diabetes.
How Emotional Well-Being Affects Diabetes Management
Emotional well-being directly influences how effectively individuals manage their diabetes. Stress, for example, triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can cause blood sugar to spike. Anxiety or depression may result in neglecting proper care, such as skipping medications or making unhealthy dietary choices. These emotional responses can create a vicious cycle, where poor mental health leads to poorer diabetes control, and vice versa.
Strategies for Nurturing Emotional Health
- Develop a Strong Support System
Connecting with friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional relief. Sharing experiences with others who understand the challenges of living with diabetes can be particularly helpful, offering both practical advice and emotional encouragement.
- Practice Mindfulness and Stress Management
Techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help manage stress levels. These activities encourage relaxation and help regulate emotional responses, leading to better mental and physical health outcomes.
- Stay Physically Active
Exercise is a powerful tool for improving mood by releasing endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good hormones. Regular physical activity also helps with blood sugar management, which in turn can reduce stress and anxiety.
- Set Realistic Goals
Avoid overwhelming yourself with unrealistic expectations. Setting small, achievable goals allows for steady progress and boosts confidence. Celebrate the wins, even the small ones, as they contribute to long-term success.
- Seek Professional Help
Sometimes emotional challenges require the guidance of a mental health professional. Counseling, therapy, or diabetes-specific mental health programs can provide coping strategies and help you better manage your emotional health.
- Educate Yourself
Understanding your condition can reduce anxiety. The more you know about diabetes and how to manage it, the more empowered and in control you’ll feel. Empowering yourself with knowledge can alleviate fear of the unknown and provide clarity.
The Mind-Body Connection
Maintaining emotional well-being isn’t just about mental health—it’s about recognizing the strong connection between the mind and body. By addressing emotional needs, diabetics can enhance their physical health, achieve better blood sugar control, and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Conclusion
For diabetics, nurturing emotional well-being is just as important as managing physical health. A holistic approach to diabetes care acknowledges the interplay between mental and physical well-being, ensuring that individuals can lead healthier, happier lives. By practicing self-care, seeking support, and managing stress, diabetics can improve their emotional health and, in turn, better manage their condition.

 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago