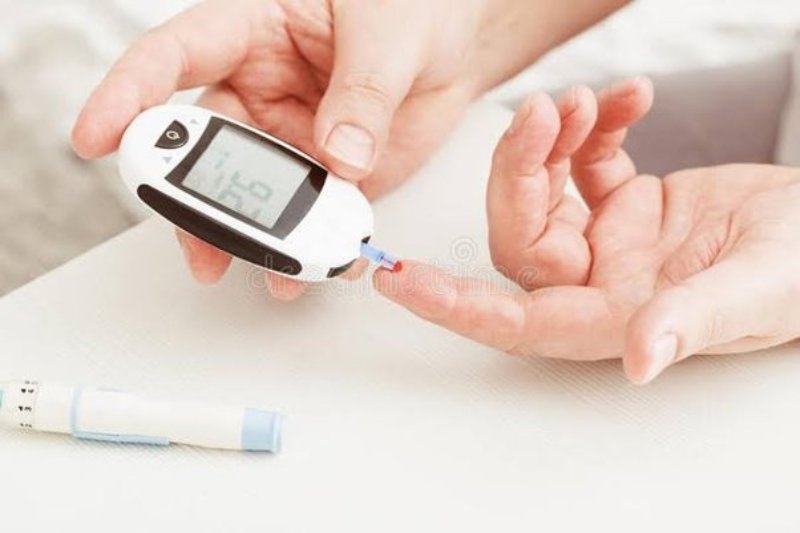
Understanding Blood Sugar and Diabetes
What is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It’s derived from the foods we eat, especially carbohydrates. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Proper blood sugar regulation is vital for normal bodily functions and overall health.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes: A condition characterized by insulin resistance, where the body doesn’t use insulin effectively. Over time, the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medication.
Gestational Diabetes: Develops during pregnancy and usually disappears after childbirth. It increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and child.
Importance of Blood Sugar Management
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent both short-term and long-term complications. Short-term complications include hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can be dangerous if not treated promptly. Long-term complications can affect various organs and systems, including the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Traditional Methods of Blood Sugar Management
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet is fundamental in managing diabetes.
Low-Carb Diets: Reducing carbohydrate intake can help lower blood sugar levels. Focus on consuming complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, which are digested slowly and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Glycemic Index and Load: The glycemic index (GI) ranks foods based on their effect on blood sugar levels. Low-GI foods cause a slower rise in blood sugar. Glycemic load (GL) considers the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a serving. Eating low-GI and low-GL foods can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Importance of Fiber: Fiber slows the digestion of carbohydrates and the absorption of sugar, helping to prevent blood sugar spikes. Include high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for managing diabetes.
Types of Exercises Beneficial for Diabetics: Aerobic exercises (like walking, cycling, and swimming) and strength training can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels.
How Exercise Helps Regulate Blood Sugar: Physical activity increases insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to use glucose more effectively. It also helps muscles absorb glucose, reducing blood sugar levels.
Medication and Insulin Therapy
Common Medications for Diabetes: Metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors are commonly prescribed to manage blood sugar levels.
Insulin Types and Administration Methods: Insulin therapy is crucial for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes necessary for Type 2 diabetes. Types of insulin include rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting. Administration methods include injections, insulin pens, and insulin pumps.
Innovative Dietary Approaches
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting.
Overview and Benefits for Blood Sugar Control: IF can improve insulin sensitivity and promote weight loss, both of which can help manage blood sugar levels. Common IF methods include the 16/8 method (16 hours of fasting and 8 hours of eating) and the 5:2 method (eating normally for 5 days and restricting calories for 2 days).
Types of Intermittent Fasting: Other methods include alternate-day fasting and the eat-stop-eat method. Choose a method that fits your lifestyle and consult with your healthcare provider before starting IF.
Plant-Based Diets
Benefits for Diabetes Management: Plant-based diets, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, are high in fiber and low in unhealthy fats, making them beneficial for blood sugar control.
Nutrient Considerations: Ensure you get enough protein, iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids from plant-based sources or supplements.
Functional Foods and Supplements
Certain foods and supplements can help manage blood sugar levels.
Cinnamon, Chromium, and Other Supplements: Cinnamon has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. Chromium, a trace mineral, can enhance the action of insulin. Other beneficial supplements include alpha-lipoic acid and magnesium.
How They Help in Managing Blood Sugar: These functional foods and supplements can improve glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, aiding in better blood sugar control.
Cutting-Edge Exercise Strategies
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
Benefits for Blood Sugar Control: HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by rest or low-intensity exercise. It can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels more effectively than moderate-intensity exercise.
Sample HIIT Routines: A typical HIIT routine might include 30 seconds of sprinting followed by 1 minute of walking, repeated for 20-30 minutes. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting HIIT.
Resistance Training
How It Helps in Managing Diabetes: Resistance training, such as weight lifting, builds muscle mass, which helps increase glucose uptake by muscles and improves insulin sensitivity.
Effective Exercises and Routines: Include exercises that target all major muscle groups, such as squats, lunges, push-ups, and deadlifts. Aim for at least two sessions per week.
Yoga and Mindfulness Practices
Stress Reduction and Blood Sugar Control: Stress can raise blood sugar levels by triggering the release of stress hormones. Yoga and mindfulness practices help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Specific Poses and Breathing Exercises: Poses like the forward bend, legs-up-the-wall, and child’s pose can help reduce stress. Incorporate deep breathing exercises and meditation to enhance the benefits.
Technological Innovations in Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
How They Work and Benefits: CGMs are devices that provide real-time blood sugar readings throughout the day. They help track patterns and trends, allowing for better blood sugar management.
Popular CGMs on the Market: Some popular CGMs include the Dexcom G6, FreeStyle Libre, and Medtronic Guardian. These devices provide alerts for high and low blood sugar levels and can sync with smartphones.
Smart Insulin Pens and Pumps
Features and Advantages: Smart insulin pens and pumps offer precise dosing, data tracking, and integration with CGMs. They can help optimize insulin therapy and improve blood sugar control.
Future Trends in Insulin Delivery Systems: Emerging technologies include artificial pancreas systems and closed-loop systems, which automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar readings.
Mobile Apps and Digital Health Tools
Best Apps for Diabetes Management: Apps like mySugr, Glucose Buddy, and BlueLoop help track blood sugar levels, medication, diet, and exercise.
How Digital Tools Can Enhance Self-Management: Digital tools provide insights, reminders, and support, making it easier to manage diabetes effectively. They can also facilitate communication with healthcare providers.
Psychological and Behavioral Strategies
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
How CBT Can Help Manage Diabetes: CBT addresses negative thought patterns and behaviors, helping individuals develop healthier coping strategies. It can reduce stress and improve adherence to diabetes management plans.
Practical Tips and Exercises: Techniques include setting realistic goals, problem-solving, and developing a positive mindset. Working with a therapist can provide personalized guidance.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Techniques for Reducing Stress: Practices like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can help lower stress levels and improve blood sugar control.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels: Reducing stress can decrease the release of stress hormones, which can lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Building a Support Network
Importance of Community and Support Groups: Connecting with others who have diabetes can provide emotional support, practical advice, and motivation.
How to Find and Engage with Support Networks: Join local or online support groups, attend diabetes education classes, and participate in community events.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Herbal Remedies and Natural Supplements
Popular Herbs and Their Effects on Blood Sugar: Herbs like fenugreek, bitter melon, and berberine have shown potential in managing blood sugar levels.
Safety and Efficacy: Always consult with your healthcare provider before using herbal remedies or supplements, as they can interact with medications.
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Overview and Benefits: Acupuncture and TCM can help improve blood sugar control and overall health by balancing the body’s energy.
Evidence and Studies Supporting TCM: Some studies suggest that acupuncture and TCM can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. More research is needed to confirm these benefits.
Lifestyle and Environmental Modifications
Sleep Hygiene and Blood Sugar: Poor sleep can affect blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
Environmental Factors Affecting Diabetes Management: Environmental factors like pollution, stress, and access to healthy foods can impact diabetes management. Make lifestyle adjustments to create a supportive environment.
Real-Life Success Stories and Case Studies
Profiles of Individuals Who Successfully Managed Diabetes
Brief Case Studies: Share stories of individuals who have successfully managed their diabetes through innovative approaches. Highlight their strategies and outcomes.
Key Takeaways and Lessons Learned: Summarize the main lessons from these success stories and provide practical tips that readers can apply to their own lives.
Innovative Programs and Initiatives
Community Programs and Their Impact: Highlight community programs and initiatives that have helped people manage diabetes effectively.
Notable Success Stories: Share examples of programs that have made a significant difference in the lives of individuals with diabetes.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Recap the innovative tips discussed in the article, including dietary approaches, exercise strategies, technological innovations, psychological and behavioral strategies, and alternative therapies.
Final Thoughts
Emphasize the importance of a holistic approach to diabetes management. Combining traditional methods with innovative strategies can lead to better blood sugar control and improved quality of life.
Call to Action
Encourage readers to explore and implement the tips discussed in the article. Consult with healthcare providers before making significant changes to their diabetes management plan.
References
Citations and Sources: List all references and sources used in the article, including scientific studies, expert opinions, and reliable websites.
Further Reading: Recommend books, articles, and resources for readers who want to learn more about managing diabetes and blood sugar levels.

 General Medicine2 weeks ago
General Medicine2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 General Medicine2 weeks ago
General Medicine2 weeks ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago