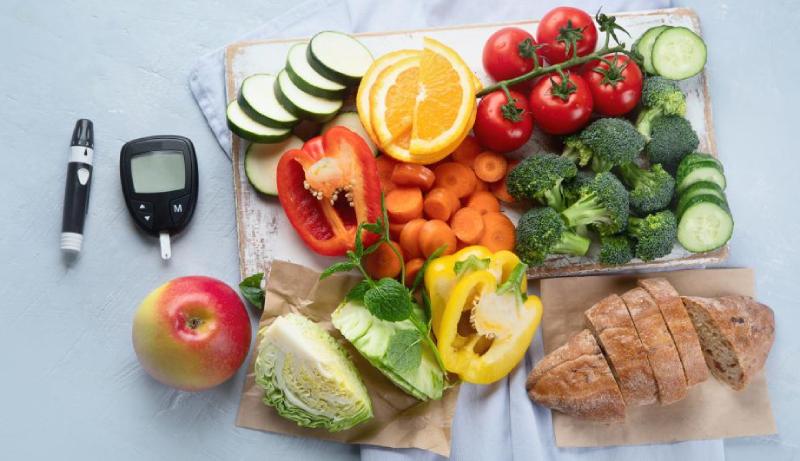
Diabetes mellitus, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, affects millions globally. Managing blood sugar is crucial to prevent complications. This review delves into the impact of protein on blood sugar control in diabetes, exploring its effects, potential benefits, and considerations for dietary planning.
Protein: A Macronutrient with Diverse Roles
Protein, alongside carbohydrates and fat, is a vital macronutrient. It serves numerous functions, including building and repairing tissues, creating enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. Unlike carbohydrates, the primary source of blood sugar (glucose), protein has a minimal direct effect.
The Intricate Relationship Between Protein and Blood Sugar
The body prioritizes carbohydrates for glucose production. However, in situations with limited carbohydrate availability, protein can be converted into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis. This process primarily occurs in the liver and kidneys.
Factors Influencing Protein’s Blood Sugar Impact
Several factors influence the extent to which protein affects blood sugar in individuals with diabetes:
Type of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: In the absence of sufficient insulin production, gluconeogenesis from protein may be elevated, potentially contributing to higher blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The impact of protein on blood sugar can vary depending on insulin sensitivity. Those with good insulin sensitivity may experience minimal effects, while those with insulin resistance may see a more pronounced rise.
- Amount of Protein Consumed: The quantity of protein ingested influences the extent of gluconeogenesis. Larger protein intakes may lead to a greater rise in blood sugar.
- Source of Protein: The type of protein source can play a role. Animal-based proteins tend to stimulate glucagon, a hormone that promotes gluconeogenesis, potentially leading to a slightly higher blood sugar response compared to plant-based proteins.
- Meal Composition: Pairing protein with carbohydrates and healthy fats can significantly impact blood sugar. Protein’s slower digestion can help slow down carbohydrate absorption, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar. Fiber-rich carbohydrates further contribute to this effect.
Potential Benefits of Protein for Diabetes Management
Despite the potential for protein to raise blood sugar, it offers several benefits for diabetes management:
- Enhanced Satiety: Protein promotes feelings of fullness and reduces hunger, potentially helping with weight management, a crucial factor in diabetes control.
- Improved Glycemic Control: Pairing protein with carbohydrates can lead to a more stable blood sugar response compared to carbohydrate-rich meals alone.
- Muscle Preservation: Adequate protein intake can help maintain muscle mass, which is often depleted in individuals with diabetes. This is particularly important for preventing complications and improving overall health.
Optimizing Protein Intake for Diabetes Management
While protein offers valuable benefits, it’s important to consider these points for optimal dietary planning:
- Individualized Needs: A healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate protein intake based on factors like age, weight, activity level, and kidney function.
- Spreading Protein Throughout the Day: Distributing protein intake across meals and snacks can help maintain a steady supply of amino acids and potentially minimize blood sugar spikes.
- Choosing Protein Sources Wisely: Opt for lean protein sources like fish, poultry, legumes, and low-fat dairy products. Limit processed meats and red meats due to their saturated fat content.
- Pairing with Fiber and Healthy Fats: Combine protein with complex carbohydrates rich in fiber and healthy fats like vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds to promote a balanced and gradual blood sugar response.
Future Directions in Protein Research for Diabetes
Research continues to explore the intricacies of protein metabolism and its impact on blood sugar control. Some areas of interest include:
- The Role of Specific Amino Acids: Understanding how different amino acids influence gluconeogenesis and insulin sensitivity may pave the way for personalized dietary recommendations.
- Impact of Protein Quality: Investigating the effect of protein quality (digestibility and amino acid composition) on blood sugar control could provide valuable insights.
- Long-Term Effects of High-Protein Diets: Further studies are needed to determine the long-term safety and efficacy of high-protein diets for diabetes management, particularly concerning potential risks for kidney health.
Conclusion
Protein plays a complex role in blood sugar control for individuals with diabetes. While it can modestly raise blood sugar through gluconeogenesis, the benefits of protein intake, including satiety, improved glycemic control, and muscle preservation, are noteworthy. By considering factors like protein source, amount, and meal composition, individuals with diabetes can leverage protein to achieve optimal blood sugar management and overall well-being.

 General Medicine2 weeks ago
General Medicine2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 General Medicine2 weeks ago
General Medicine2 weeks ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago





