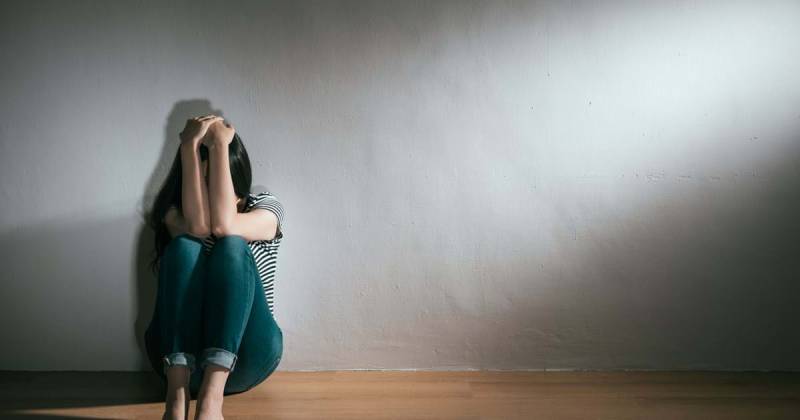
Diabetes is a chronic condition that not only affects blood sugar levels but also significantly impacts a person’s emotional well-being. The constant pressure of managing the disease, combined with the fear of complications, can take a toll on mental health. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate link between diabetes and psychological well-being, empowering you with information and strategies to navigate the emotional rollercoaster that often accompanies this condition.
The Emotional Landscape of Diabetes
Living with diabetes is a complex journey filled with a multitude of emotions. Here’s a closer look at some of the most common psychological struggles faced by diabetics:
- Diagnosis Shock: Receiving a diabetes diagnosis can be overwhelming, leading to feelings of fear, anxiety, and uncertainty about the future.
- Denial and Anger: Some individuals may initially deny the diagnosis or experience anger towards themselves or their circumstances.
- Frustration and Discouragement: Managing diabetes requires constant vigilance and lifestyle changes. Setbacks and difficulties with blood sugar control can lead to frustration and discouragement.
- Isolation and Loneliness: The fear of judgment or feeling different can lead to social isolation and feelings of loneliness.
- Depression and Anxiety: The chronic nature of the disease, along with the fear of complications, can significantly increase the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Eating Disorders: The focus on food and blood sugar control can sometimes lead to developing unhealthy relationships with food, such as disordered eating habits.
- Body Image Issues: Changes in weight or physical appearance due to diabetes can negatively impact body image and self-esteem.
Understanding Diabetes Distress
Beyond specific diagnoses like depression or anxiety, a distinct phenomenon known as “diabetes distress” is prevalent. It encompasses the emotional and psychological burden associated with managing diabetes. Symptoms may include:
- Constant worry about blood sugar levels
- Feeling overwhelmed by the demands of self-care
- Frustration with treatment regimens
- Guilt or shame over blood sugar fluctuations
- Fear of developing complications
Factors Contributing to Psychological Issues
Several factors contribute to the psychological impact of diabetes:
- Chronic Illness Burden: Diabetes requires constant management, creating a sense of burden and stress.
- Fear of Complications: The potential for serious health complications associated with diabetes can be a significant source of anxiety.
- Loss of Control: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can create a sense of loss of control over one’s health.
- Social Stigma: Misconceptions about diabetes can lead to social stigma, contributing to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Financial Concerns: Managing diabetes can be expensive, leading to financial stress and anxiety.
Building Resilience and Navigating Challenges
The good news is that there are effective tools and strategies to manage the emotional impact of diabetes. Here are some steps you can take:
- Acknowledge Your Emotions: It’s important to acknowledge and validate your emotions. Sharing your feelings with loved ones, a therapist, or a support group can be immensely helpful.
- Learn About Diabetes: The more you know about your condition, the better equipped you are to manage it effectively and reduce fear and anxiety.
- Develop Coping Mechanisms: Healthy coping mechanisms like relaxation techniques, mindfulness exercises, and physical activity can help manage stress and improve emotional well-being.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of diabetes can provide invaluable support, encouragement, and a sense of belonging.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Taking care of yourself physically and emotionally is crucial. Prioritize getting enough sleep, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in activities you enjoy.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re struggling with overwhelming emotions or suspect you may have depression or anxiety, don’t hesitate to seek professional help from a therapist or counselor.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in supporting the emotional well-being of their diabetic patients. Here’s what you can expect from your doctor:
- Open Communication: Discuss your emotional struggles openly with your doctor. They can address your concerns and provide support or referrals to mental health professionals.
- Empathy and Understanding: A caring and supportive healthcare team can make a significant difference in your emotional well-being.
- Holistic Care Approach: Treatment plans should address both the physical and emotional aspects of diabetes management.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Diabetes
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but it doesn’t have to define your life. By understanding the emotional impact of the condition, developing coping mechanisms, and prioritizing your mental well-being, you can navigate the challenges and live a fulfilling life.
Living a Fulfilling Life with Diabetes:
- Empower Yourself with Knowledge: Stay informed about the latest advancements in diabetes management, research, and support resources.
- Celebrate Your Victories: Focus on the positive aspects of managing your diabetes. Celebrate even small victories, like maintaining good blood sugar control or sticking to your exercise routine.
- Maintain a Positive Attitude: A positive outlook can significantly improve your coping abilities and overall well-being. Focus on what you can control and celebrate all the ways you take charge of your health.
- Find Your Voice: Advocate for yourself and others with diabetes. Share your story and raise awareness about the challenges and triumphs associated with the condition.
Looking Towards a Brighter Future
Significant advancements are being made in diabetes research, offering hope for a future with better management tools and even potential cures. However, for now, focusing on emotional well-being and adopting a self-care approach remain crucial aspects of living well with diabetes.
Note: This guide is intended for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare professional for personalized recommendations regarding managing your diabetes and your mental health.

 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago
 Diabetology3 days ago
Diabetology3 days ago
 Diabetology5 days ago
Diabetology5 days ago









