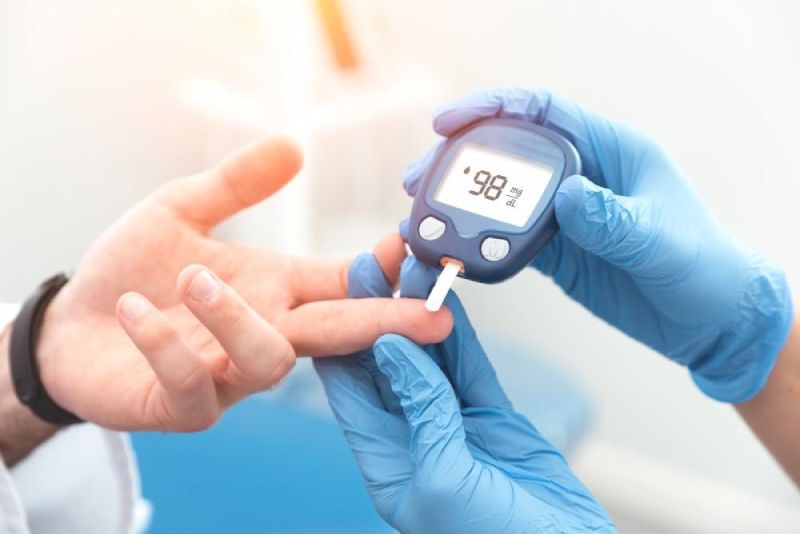
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions globally. It disrupts how your body regulates blood sugar (glucose) levels, leading to a variety of health problems if left unaddressed. Early detection is crucial for effective management and preventing complications. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of diabetes, their early warning signs, and strategies for seeking timely diagnosis.
Understanding Diabetes: A Spectrum of Conditions
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): An autoimmune disease where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The body cannot produce enough insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. T1D typically manifests in childhood or adolescence.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, where the body either resists the effects of insulin (insulin resistance) or doesn’t produce enough. It often develops gradually and can go undiagnosed for years, particularly in the early stages.
- Gestational Diabetes: A temporary form of diabetes occurring during pregnancy. While it usually resolves after childbirth, women with gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Early Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
While symptoms can vary depending on the type of diabetes and its severity, several early warning signs are common across different forms:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: The body excretes excess sugar through urine, leading to frequent urination and increased thirst to replenish fluids.
- Excessive Hunger: Cells are starved for energy due to insufficient insulin, leading to constant hunger pangs despite adequate calorie intake.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: The body may break down muscle and fat for energy when it cannot utilize blood sugar effectively, leading to unintentional weight loss, particularly in T1D.
- Fatigue and Lethargy: Cells deprived of glucose, the primary energy source, can cause chronic fatigue and tiredness.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurry vision or difficulty focusing.
- Slow Healing Wounds: Diabetes can impair blood circulation and the body’s ability to heal wounds. Cuts, scrapes, or infections may take longer to heal or become recurrent.
- Frequent Skin Infections: High blood sugar levels create a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi, leading to frequent skin infections like boils, abscesses, or yeast infections.
- Increased Itching: Dry, itchy skin can be a symptom of high blood sugar or yeast infections commonly associated with diabetes.
- Tingling or Numbness: High blood sugar can damage nerves, particularly in the hands and feet, leading to tingling, numbness, or pain.
Risk Factors: Knowing Who’s More Susceptible
While anyone can develop diabetes, some individuals have a higher risk:
- Family History: Having a parent or sibling with diabetes significantly increases your risk.
- Overweight or Obesity: Being overweight, particularly carrying excess fat around the abdomen, increases insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to insulin resistance and weight gain, both risk factors for diabetes.
- Prediabetes: A precursor to diabetes, characterized by mildly elevated blood sugar levels.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in Women: This hormonal imbalance can increase insulin resistance and diabetes risk.
- Gestational Diabetes: Women with a history of gestational diabetes have a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Don’t Wait Until Symptoms Become Severe
Early symptoms of diabetes can be subtle and easily dismissed. However, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience any of the warning signs mentioned above, especially if you have multiple risk factors.
- Early diagnosis is critical for preventing complications like heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems.
- Early intervention allows for timely treatment and lifestyle modifications to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Seeking Diagnosis: Your Healthcare Partner
If you suspect you or someone you know might have diabetes, schedule an appointment with your doctor. They will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including:
- Detailed medical history to understand your symptoms, risk factors, and family history.
- Physical examination to assess overall health and check for signs of diabetes-related complications.
- Blood tests like fasting blood sugar test, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test, and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to measure blood sugar levels and diagnose diabetes.
Taking Control: Managing Diabetes Effectively
Once diagnosed, your doctor will develop a personalized treatment plan to manage your diabetes, which may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: weight management (if needed) are crucial for optimal blood sugar control.
- Medications: Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, medications like insulin injections, oral medications, or a combination may be prescribed.
- Blood sugar monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring with a glucometer at home helps you understand your body’s response to food, exercise, and medication.
- Diabetes education: Learning about diabetes management, self-care practices, and potential complications empowers you to take control of your health.
- Ongoing medical care: Regular checkups with your doctor are essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans as needed, and prevent complications.
Living Well with Diabetes: A Supportive Community
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but you’re not alone. Here are resources to support you on your journey:
- Support groups: Connecting with others who understand your challenges can provide emotional support, motivation, and shared experiences.
- Online communities: Numerous online forums and social media groups connect individuals with diabetes. Access information, share experiences, and build a virtual support network.
- Mental health support: Living with a chronic condition can take an emotional toll. Consider seeking mental health support if needed.
- Diabetes educators and registered dietitians: These professionals provide invaluable guidance on managing your diabetes through dietary modifications and lifestyle changes.
Be Your Own Advocate: Knowledge is Power
- Stay informed: Educate yourself about diabetes, its different types, risk factors, and treatment options.
- Participate in research: Consider joining research studies that aim to improve diabetes treatment and prevention.
- Advocate for change: Support initiatives that raise awareness, promote access to affordable healthcare and medications, and fund research for a potential cure.
Remember, early detection is key to managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications. By being aware of the warning signs, understanding your risk factors, and seeking prompt medical attention, you can take control of your health and live a fulfilling life.

 General Medicine2 weeks ago
General Medicine2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago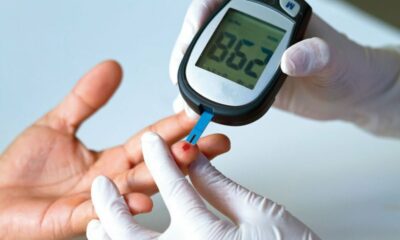
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 General Medicine2 weeks ago
General Medicine2 weeks ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology6 days ago
Diabetology6 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago






