Dermatology
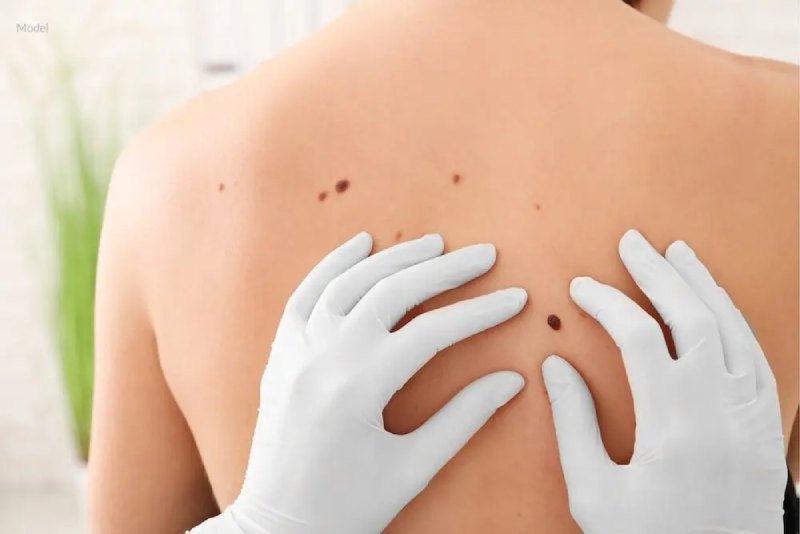
What You Should Know About Skin Cancer and Sunlight
-

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoHot Weather Impacts Blood Sugar: Essential Tips to Stay Balanced
-

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoHow Carbs Impact Blood Sugar and Smart Ways to Manage Them
-

 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoFasting With Diabetes: Essential Tips for a Healthy Ramadan
-

 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week agoCDC Warns About Rising Dengue Fever Threat: Symptoms and Prevention Tips
-
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks agoEight Physical Clues Can Develop Your Body Diabetes
-

 General Medicine1 week ago
General Medicine1 week agoThe Rise of ‘Sleepmaxxing’: Evaluating 2025’s Viral Sleep Optimization Trends
-

 Diabetology2 days ago
Diabetology2 days agoUnderstanding Hyperglycemia: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Effective Treatment
-

 Diabetology2 days ago
Diabetology2 days agoTop 15 Low Glycemic Index Foods for Better Blood Sugar Control