A group of specialists from the Indian Organizations of Innovation (IIT) Bhilai has effectively designed an original hydrogel-based insulin-conveyance stage, which can assist patients with Type-1 diabetes better deal with their circumstances.
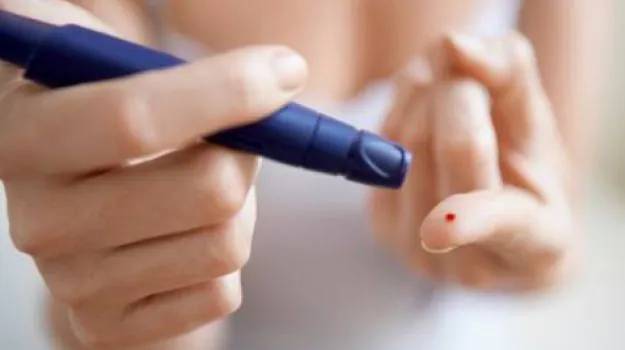
Presently, an expected 3,000,000 individuals in India depend on insulin treatment, where they frequently resort to day to day insulin infusions utilizing needles or concentrated gadgets to deal with their glucose levels.
The hydrogel-based drug conveyance framework can deliver insulin in a controlled way because of raised blood glucose levels-impersonating the normal insulin discharge cycle of sound pancreatic cells.
“Current insulin injection methods have some limitations. They do not work quite like the body’s natural system and can be fatal. The current insulin injection methods can also make blood sugar levels drop dangerously low, and patients might have to rely on them forever,” said Dr Suchetan Pal, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT Bhilai, in a statement.
The group has itemized the new framework in the diary Applied Materials and Connection points.
Utilizing the imaginative utilization of hydrogels, the new conveyance framework guarantees a protected and proficient strategy for providing insulin to insulin-subordinate diabetic patients.
Hydrogels are biocompatible polymers that are described by high water content and are being read up for controlled drug discharge in different clinical fields including cardiology, oncology, immunology, wound recuperating, and torment the executives.
The analysts typified insulin in uniquely planned hydrogels that can be managed rather than direct insulin infusions.
Drawing motivation from the body’s normal insulin discharge process set off by glucose, the group planned the hydrogels with the end goal that they would deliver insulin when glucose levels are raised.
This was accomplished by crosslinking polyvinyl liquor with small particles of chitosan, a fixing got from shellfish and crabs’ external skeletons.
The crosslinker, formylphenylboronic corrosive (FPBA), answers glucose levels and deliveries the insulin that is epitomized inside the hydrogel.
Through complete analyses including little particle drug analogs and macromolecular insulin, the group showed that the hydrogels delivered insulin dominatingly under hyperglycemic (high glucose) conditions.
The wellbeing and antidiabetic viability of insulin-stacked hydrogels were affirmed through tests in a Sort I rodent model.
“These modular hydrogels can take the form of microneedles or oral formulations and can prove sustained delivery of insulin in response to elevated blood glucose levels. This could significantly enhance convenience and safety for patients requiring insulin therapy,” Dr Pal added.

 Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Uncategorized2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology2 weeks ago
Diabetology2 weeks ago
 Diabetology1 week ago
Diabetology1 week ago
 Diabetology4 days ago
Diabetology4 days ago
 Diabetology17 hours ago
Diabetology17 hours ago
 Diabetology11 hours ago
Diabetology11 hours ago